Test: Ecological Pyramids (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Ecological Pyramids (NCERT)
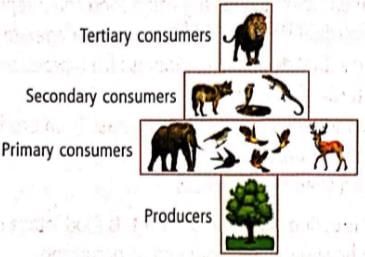
Which kind of pyramid is represented by the given figure?

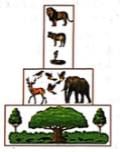
What kind of pyramid is represented by the given figure?

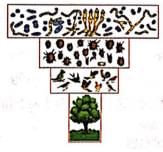
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: In an aquatic ecosystem, pyramid of biomass is inverted.
Statement 2: Biomass depends upon reproductive potential and longevity of individuals.
Study the following statements and select the incorrect one.
Given figure represents a pyramid of biomass in an aquatic ecosystem
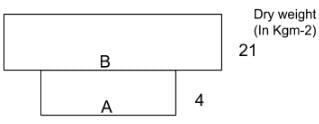
Identify A and B and select the correct answer.
(i) A is the crop which supports and B is the crop which is supported.
(ii) A is the crop which is supported and B is the crop which supports.
(iii) A is phytoplanktons and B is zooplanktons.
(iv) A is zooplanktons and B is phytoplanktons.
In an open ocean, the biomass of primary producers (microscopic algae) is often lower than the biomass of higher trophic levels (zooplanktons and fish), as illustrated below by an inverted pyramid of biomass. How can there be enough food in an open ocean to support the higher trophic levels?
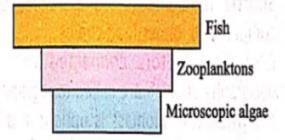
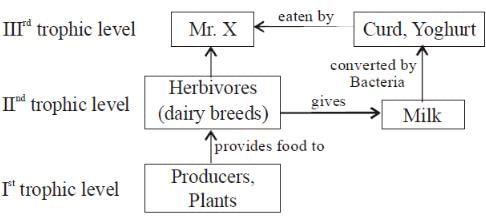
Mr. X is eating curd/yoghurt. For this food intake in a food chain he should be considered as occupying
Study the following ecological pyramids carefully.
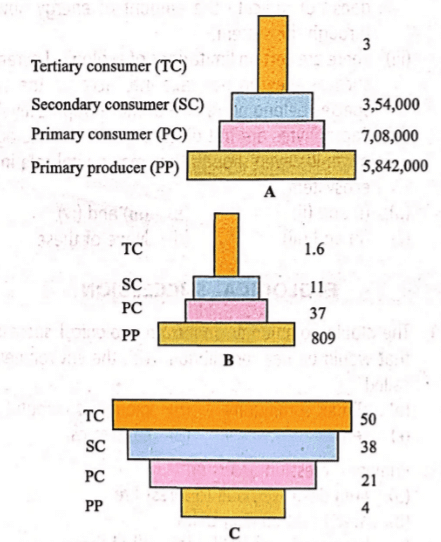
Match the following statements (i),(ii) and (iii) with given pyramids A, B and C and select the correct answer.
(i) Inverted pyramid of biomass depicting small standing crop of phytoplanktons supporting a large standing crop of zooplanktons
(ii) Pyramid of numbers in a grassland ecosystem showing about 6 million producers
(iii) Upright pyramid of biomass
Study the following statements and select the incorrect ones.
(i) Pyramids of energy and yearly biomass production can never be inverted, since this would violate the laws of thermodynamics.
(ii) Pyramids of standing crop and numbers can be inverted, since the number of organisms at a time does not indicate the amount of energy flowing through the system.
(iii) There are certain limitations of ecological pyramids such as they do not take into account the same species belonging to two or more trophic levels.
(iv) Saprophytes are not given any place in ecological pyramids even though they play a vital role in the ecosystem.
|
78 videos|277 docs|174 tests
|