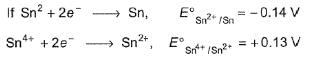Test: Electrochemical Series - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Test: Electrochemical Series
Only One Option Correct Type
This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Cl2 gas is passed into a solution containing KF, Kl and KBr, and CHCI3 is added. There is a colour in CHCI3 (lower) layer. It is due to
Select the correct statement(s) about galvanic cell (Daniell cell) with E° cell = 1.10 V
Given,
E° Ag+/Ag = 0.80 V
E° Mg2+/Mg = -2.37 V
E° Cu2+/Cu = + 0.34V
E° Hg2+/Hg = 0.79V
Q.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
E° Mg2+/Mg = -2.37 V
E° Cu2+/Cu = + 0.34V
E° Hg2+/Hg = 0.79V
One mole of Ag2CO3 is strongly heated in an open vessel. Residue wll be
Zinc ,silver and iron plates are dipped in CuSO4 solutions placed in different vessels as shown:
Blue colour of CuSO4 fades in
For the following half -cell reactions ,E° values are:
Mn2+(aq) + 2H2O(l)  MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2e-, E0 = -1.23V
MnO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2e-, E0 = -1.23V
MnO-4 (aq) + 4H+(aq) +3e-  MnO2(s) + 2H2O(l), E0 = +1.70 V
MnO2(s) + 2H2O(l), E0 = +1.70 V
Thus
Consider some facts about Standard Hydrogen Electrode(SHE).
I. It is assigned a zero potential at all temperature corresponding to the reaction.
II. Platinum electrode coated with platinum black is dipped in acidic solution and H2 gas is bubbled through it.
III. Concentration of both are oxidised and reduced forms of hydrogen is maintained at unity.
Select the correct facts
The gas X at 1 atm is bubbled through a solution containing a mixture of 1 M Y- and 1 M Z- at 298 K.If the standard reduction potential
then,
The standard reduction potential values of three metallic cations X, Y, Z are 0.52, -3.03 and -1.18 V respectively. The order of reducing power of the corresponding metals is
A solution containing one mole per litre each of Cu(NO3)2 ,AgNO3 ,Hg2(NO3)2 and Mg(NO3)2 is being electrolysed using inert electrodes. The value of standard redution potentials are
with increasing voltage , the sequence of deposition of metals on the cathode will be
The standard reduction potentials at 298K for the following half-cell are given
Which is the strongest reducing agent?
The Eo M3+/M2+ values for Cr, Mn, Fe and Co are - 0.41 V, +1,57 V, + 0.77 V and m /m 1.97 V respectively. For which one of these metals the change in oxidation state from +2 to +3 is easiest?
Given the standard electrode potentials
I. K+/K = -2.93V,
II. Ag+/Ag = 0.80V,
III. Hg2+/Hg = 0.79 V
IV. Mg2+/Mg = -2.37V,
V. Cr3+/Cr = - 0.74 V
These metals are arranged in increasing reducing power as
Statement Type
Direction : This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Statement I : CuSO4 can be stored in a vessel made of zinc.
Statement II : w.r.t SHE
Statement I : When AgNO3 solution is stirred with a spoon made of copper,solution turns blue.
Statement II : In electrochemical series ,copper is above silver
The positive value of the standard electrode potential of Cu2+/Cu,
(E°Cu2+/Cu = 0.34 V) indicates that
Consider the following half-reactions:
Select the correct statements on the basis of the above data
Select the correct statement(s) based on the following half-reaction:
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|