Test: Electrophilic Substitution Reactions - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electrophilic Substitution Reactions
During nitration of benzene, the active nitrating agent is:
The halogen which is most reactive in the halogenation of alkanes under sunlight is:
Identify the correct order of reactivity in electrophilic substitution reactions of the following compounds Benzene, methyl benzene, Chlorobenzene, nitro benzene:
Necessary condition for halogenation in benzene is:
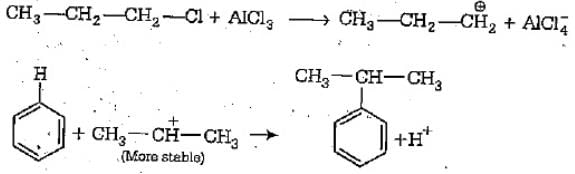
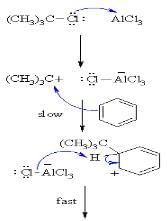
The function of anhydrous AlCl3 in the Friedel-Crafts reaction is to:
The function of AlCl3 in the Friedel Crafts reaction is:
Nitration of benzene by nitric acid and sulphuric acid is:
The compound which is most reactive towards electrophilic substitution is:
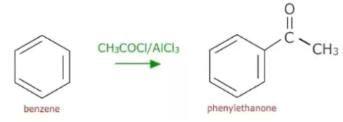
Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl and anhyd. AlCl3 gives:
The compound that is more reactive towards electrophilic nitration: