Test: Energy Flow (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Energy Flow (NCERT)
Given figure represents food chains of a deciduous woodland linked together to form a food web.

Which of the following constitute first trophic level of the grazing food chain and the detritus food chain respectively?

Study the food web given below and answer the questions that follow.
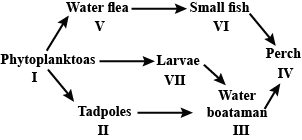
Which of the following organisms in the given food web acts as a secondary consumer?

Percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) in the incident solar radiation is
Percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) that is captured by plants in synthesis of organic matter is?
Read the following statements and select the correct ones.
(i) A given species may occupy more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem at the same time.
(ii) Productivity of an aquatic ecosystem is less than that of a terrestrial ecosystem.
(iii) Producers constitute the first trophic level of a detritus food chain.
If 10 joules of energy is available at the producer level, then amount of energy present at the level of secondary consumer is
Organisms which are associated with first as well as third trophic level are
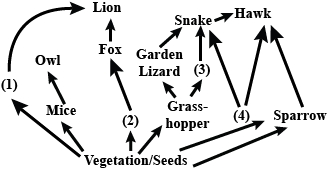
In the given food web, an increase in the population of hawks will not result in
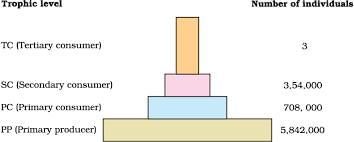
In a grassland ecosystem, if the number of primary producers is approximately 6 million plants, the number of the top carnivores (in million), which may be supported by it may be ________ million.
Which one of the following animals may occupy more than one trophic levels in the same ecosystem at the same time?
Given food web contains some missing organisms, (1), (2), (3) and (4). Identify these organisms and select the correct answer.
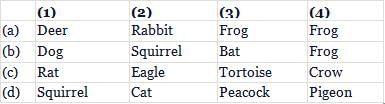
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.

In an aquatic ecosystem, the organism present at the trophic level equivalent to cows in grasslands is?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Herbivores are also called as first-order consumers.
Statement 2: Herbivores obtain their food directly from plants.
|
78 videos|277 docs|174 tests
|