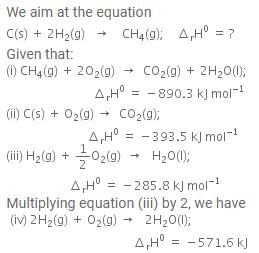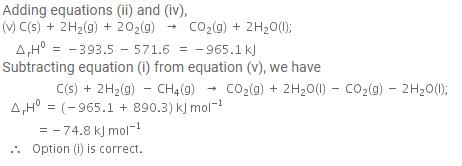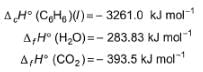Test: Enthalpy of Combustion - NEET MCQ
17 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Enthalpy of Combustion
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-11) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Calorific value of H2 is - 143 kJ g-1.Thus, ΔfH° of H2O is
In the complete combustion of C2H6, 54 g of H2O is formed and 370 kcal of heat is evolved. Thus, ΔCH° of C2H6 is
The enthalpy of combustion of methane, graphite and dihydrogen at 298 K are - 890.3 kJ mol-1, - 393.5 kJ mol-1 and - 285.8 kJ mol-1 respectively. Enthalpy of formation of CH4(g) will be
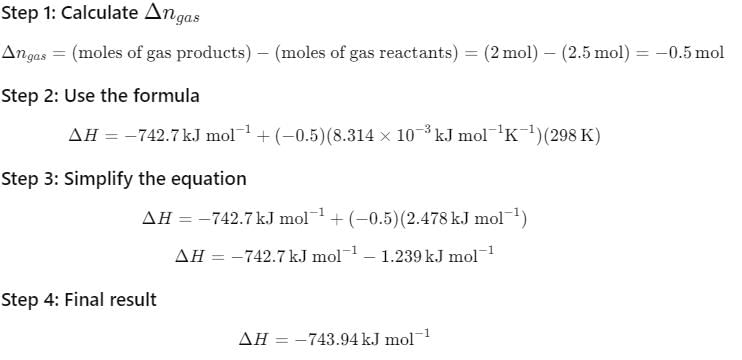
The reaction of cyanamide, NH2CN (s) was carried out in a bomb calorimeter, and ΔU was found to be - 742.7 kJ mol-1 at 298 K. Thus, ΔrH° at 298 K for
Based on the following thermochemical reactions at 298 K and 1 bar
Q. Enthalpy of vaporisation of H2O (l) is
For the following combustion reaction of benzoic acid at 298 K
Q. Thus enthalpy of combustion ΔCH° at 298 K is
The standard enthalpies of formation of CO2(g), H2O (l) and glucose (s) at 25°C are - 400 kJ mol-1, - 300 kJ mol-1 and - 1300 kJ mol-1 respectively. The standard enthalpy of combustion per gram of glucose at 25°C is
[JEE Advanced 2013]
For the complete combustion of ethanol,
the amount of heat produced as measured in bomb calorimeter is 1364.47 kJ mol-1 at 25°C. Assuming ideality, the enthalpy of combustion, ΔCH° for the reaction Will be (R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1)
[JEE Main 2014]
ΔfU° of formation of CH4(g) at a certain temperature is - 393 kJ mol-1. The value of ΔfH° is
Heat of combustion of H2(g) is - 58 kcal mol-1 at 298 K and constant pressure.
Q. Temperature of a hydrogen-oxygen flame if H2(g) is used as fuel is
Direction (Q. Nos. 12-15) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d).
Passage I
Octane (C8H18), a primary constituent of gasoline, burns in air
A 1.00 g sample of octane is burned in a constant volume calorimeter containing 1.20 kg of water. The temperature of water and the bomb rises by 8.2 K. The heat capacity of the bomb is 837.0 JK-1. Molar heat capacity of water is 4.184 J g-1 K-1. Initial temperature is 298 K.
Q. ΔCU° (per mol of C8H18) is
Passage I
Octane (C8H18), a primary constituent of gasoline, burns in air
A 1.00 g sample of octane is burned in a constant volume calorimeter containing 1.20 kg of water. The temperature of water and the bomb rises by 8.2 K. The heat capacity of the bomb is 837.0 JK-1. Molar heat capacity of water is 4.184 J g-1 K-1. Initial temperature is 298 K.
Q. ΔCH° (per mol of C8H18) is
Passage II
Heat of combustion of sucrose under standard state is - 5640 kJ mol-1. A healthy person takes 20 breaths per minute, and each breath consumer 480 mL of air. Inhaled and exhaled air contains 20% and 15% of oxygen by volume.
Q. If oxygen retained in the body is used in the combustion of sucrose, number of moles of sucrose combusted per day is
Passage II
Heat of combustion of sucrose under standard state is - 5640 kJ mol-1. A healthy person takes 20 breaths per minute, and each breath consumer 480 mL of air. Inhaled and exhaled air contains 20% and 15% of oxygen by volume.
Q. Heat evolved as a result of combustion of sucrose is
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. Given, ΔfH° of the following in kJ mol-1.
Determine the ratio taking derived values per unit volume of fuel
ΔCH° (cyclopropane) = - 2091.97 kJ mol-1
ΔCH° (propene) = - 2058.32 kJ mol-1
Q. What is ΔrH° (in kcal) propene → cyclopropane?