Test: Enthalpy of Neutralisation & Solution - NEET MCQ
19 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Test: Enthalpy of Neutralisation & Solution
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains 13 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. If the enthalpy of HCI (g) and Cl- (aq) are - 92.30 kJ mol-1 and - 167.44 kJ mol-1 respectively, then ΔrH° for the following reaction is
HCI (g) + aq → H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq)
The enthalpy of neutralisation of HS- (aq) is - 5.1 kJ mol-1. Thus, second ionisation energy of H2S is
Given, ΔfH° of HCI (g) is - 22 . 10 kcal mol-1 and ΔSolutionH° (heat of solution) of HCI (g) is - 17.9 kcal mol-1. Thus, ΔfH ° of Cl- (aq) is
Enthalpy of neutralisation of a weak dibasic acid by NaOH is - 24.0 kcal. Thus, enthalpy of ionisation of dibasic acid is
Consider the following reaction,
30 mL of 0.10 MNaOH (aq) + 10 mL of 0.10 M HCI (aq), enthalpy change is .
On further adding 20 mL of 0.10 M HCI (aq), enthalpy change is . Thus, these values are
In the following reactions,
I. 30 mL of 0.1 M Ba(OH)2(aq) + 30 mL of 0.1 M H2SO4 (aq), rise intemperature = ΔT1
II. 90 mL of 0.1 M Ba(OH)2(aq) + 90 mL of 0.1 M H2SO4 (aq), rise intemperature = ΔT2. Thus,
Given, CH3COOH(aq) → CH3COO- (aq) + H+ (aq), ΔrH° = 0.005 kcal g-1
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of Ca(OH)2, a strong base, is completely neutralised by CH3COOH (aq) in dilute solution is
Thus, heat of neutralisation of H2C2O4 (aq) is
Given,
Thus, for the reaction,
ΔrH° is
Hydration energies of Li+ and Cl- ions are - 499 and - 382 kJ mol-1 respectively. If lattice energy of LiCI is - 840 kJ mol-1 then heat of solution of LiCI is
Enthalpy change on mixing 100 mL of 1 M Ca(OH)2 with 100 mL of 1 M H2SO4 is
Taking each reactant in 1:1 molar ratio, enthalpy changes are and
in the following reactions.
and
are (in kcal)
Direction (Q. Nos. 14) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.
Q. Statement I : Based on the following thermochemical reactions :
Ionisation of HF(aq)is an exothermic reaction.
Statement II : Enthalpy decrease in hydration of H+ (aq) and F- (aq) exceeds the ionisation energy of HF.
Direction (Q. Nos. 15-16) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d).
A quantity of 100 mL of 0.5 HCI is mixed with the 100 mL of 0.5 NaOH in a constant pressure calorimeter that has a heat capacity of 335 JK-1. Temperature of the mixture increased by 2.40 K. Density of the solution = 1g mL-1.
Q. Heat of solution due to mixing is
A quantity of 100 mL of 0.5 HCI is mixed with the 100 mL of 0.5 NaOH in a constant pressure calorimeter that has a heat capacity of 335 JK-1. Temperature of the mixture increased by 2.40 K. Density of the solution = 1g mL-1.
Q. Heat of neutralisation per mole of each reactant is
Direction (Q. Nos. 17 - 19) This section contains 3 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. Lattice energy of NaCI (s) is - 788.0 kJ mol-1 and enthalpy of hydration is - 784.0 kJ mol-1. What is enthalpy change for the following reaction in kJ mol-1?
When 4.0 mL of 2.0 N solution of weak acid is neutralised by a dilute aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide, 64 cal of heat is liberated. What is the heat of neutralisation in cal/milliequivalent?
Heat of neutralisation of a polybasic acid by a strong base is - 54.8 kcal mol-1? What is basicity of the acid?
|
9 docs|1259 tests
|



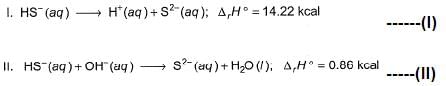
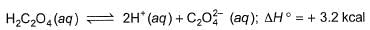
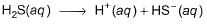
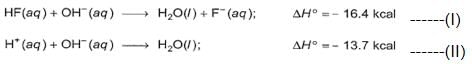 On (I) - (II), we have
On (I) - (II), we have
















