Test: Evidences of Evolution (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Evidences of Evolution (NCERT)
In the developmental history of mammalian heart, it is observed that it passes through a two chambered fish like heart, three chambered frog like heart and finally four chambered stage
To which hypothesis can this above cited statement be approximated?
To which hypothesis can this above cited statement be approximated?
Which one of the following describes correctly the homologous structures?
In evolution, the studies can be made at molecular level. For example, the proteins present in the blood of man and ape are similar. The base sequence in nucleic acids and amino acids sequence in proteins of related organism is alike. These are the examples which are specifically referred to in
The wings of a bird and the wings of an insect are :
A population will not exist in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium if
Forelimbs of cat, lizard used in walking, forelimbs of whale used in swimming and forelimbs of bats used in flying are an example of:
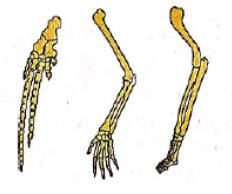
What can you infer about the structures shown in figure?
|
78 videos|277 docs|174 tests
|