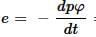Test: Faraday’s Laws of Induction - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Physics Class 12 - Test: Faraday’s Laws of Induction
A magnet is moved towards the coil (i) quickly, (ii) slowly, the induced emf is
The magnetic flux linked with a coil is changed from 1 Wb to 0.1 Wb in 0.1 second. The induced emf is
The principle of electromagnetic induction is used in which of the following phenomenon
Which of the following law’s gives the direction of induced emf?
In the expression, what is the significance of negative sign?
Magnetic flux φ in Weber in closed circuit of resistance 15 ohm varies with time t sec as φ = 2t² – 3t + 1. The magnitude of induced emf at t = 0.25 sec is
If the North Pole of the bar magnet is introduced into a coil at the end A which of the following statements correctly depicts the phenomenon taking place.
In which of the following cases with a bar magnet and the coil no induced emf is induced.
A coil of 100 turns is pulled in 0.04 sec. between the poles of a magnet, if its flux changes from 40 x 10-6 Wb per turn to 10-5 Wb per turn, then the average emf induced in the coil is
|
98 videos|334 docs|102 tests
|