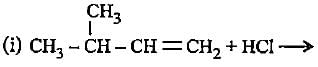Test: Fundamental Concepts in Organic Reaction Mechanism (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions - Test: Fundamental Concepts in Organic Reaction Mechanism (NCERT)
Heterolysis of a carbon-chlorine bond produces
Which of the following is an electrophilic reagent?
Which of the following sets of groups contains only electrophiles?
Inductive effect involves
The increasing order of electron donating inductive effect of alkyl groups is
Inductive effect of which atom or group is taken as zero to compare inductive effect of other atoms?
Maximum -I effect is exerted by the group
Which one of the following acids would you expect to be the strongest?
Few pairs of molecules are given below. Which bond of the molecule of the pairs is more polar?
(i) H3C - H, H3C - Br
(ii) H3C-NH2,H3C-0H
(iii) H3C - OH, H3C - SH
(iv) H3C - Cl, H3C - Br
Which of the following is the correctorder of acidity of carboxylic acids?
(i) CI3CCOOH > CI2CHCOOH > CICH2COOH
(ii) CH3CH2COOH > (CH3)2CHCOOH > CCH3)3CCOOH
(iii) F2CHCOOH > FCH2COOH > CICH2COOH
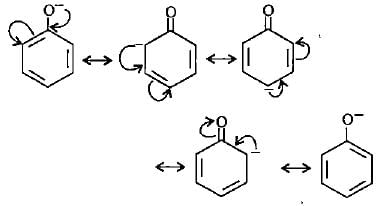
Point out the incorrect statement about resonance?
Which of the following ions is the most resonance stabilised?
Hyperconjugation is
The number of hyperconjugating structures shown by the carbocations are given below. Which one is not correctly matched?
In which of the following species hyperconjugation is possible?
Answer the following question based on the given paragraph.
Stability of carbocation, alkylfree radical and alkene can be explained on the basis of hyperconjugation.
In all these cases, there is presence ofhydrogen atom at theadjacent carbon atom ofsp2 hybridised carbon atom. Total number of hyperconjugating structures depends upon the number of hydrogen atoms present at adjacent carbon atom of sp2 C-atom.
More the hyperconjugating structures, more is the stabihty of the ion.
Decreasingorder of stabilityof following alkenes is
(i) CH3 - CH = CH2
(ii) CH3 - CH = CH - CH3
(iii) 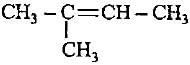
(iv) 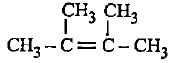
Which of the following alcohols on dehydration gives most stable carbocation?
Which of the following contains three pairs of electrons in valence shell?
Stability of alkyl carbocations can be explained by
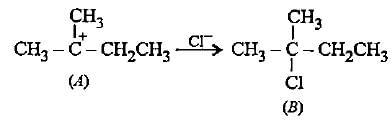
In the given reaction two products are expected.
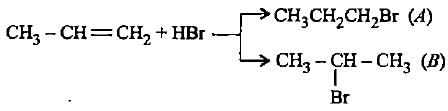
The product (B) is formed as a major product because
The carbocation 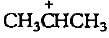 is less stable than
is less stable than
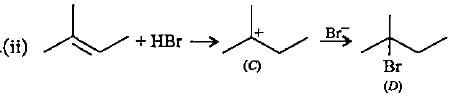
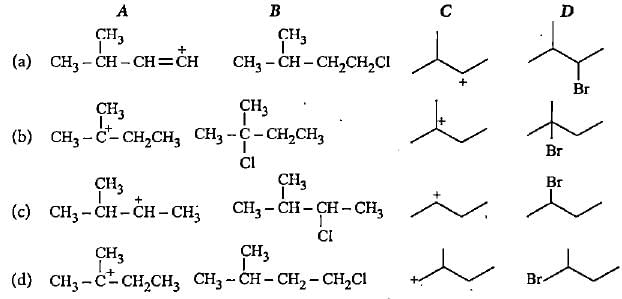
Complete the following reactions by filling most stable intermediate and the product.
(i) 
(ii) 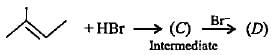
Which of the following statements is not true about the stability of carbanions?
Which of the following carbanion expected to be most stable?
The order of decreasing stability of the following carbanions is
(i) (CH3)3C-
(ii) (CH3)2CH-
(iii) CH3CH-2
(iv) C6H5CH-2
Free radicals can undergo
The most stable free radical among the following Is
Which of the following Is a characteristic feature of a free radical?
The increasing order of stability of the following free radicals is
Which of the following is a false statement?
|
257 docs|234 tests
|



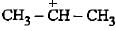 shows 6 hyperconjuigatihg structures
shows 6 hyperconjuigatihg structures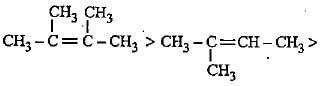
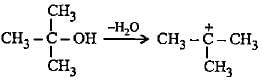
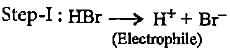
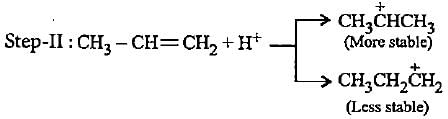
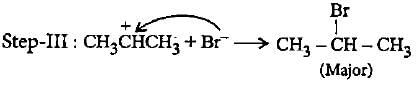
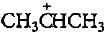 . Rest all are primary carbocations hence less stable.
. Rest all are primary carbocations hence less stable.