Test: Growth and Development (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Growth and Development (NCERT)
An irreversible or permanent increase in size, mass or volume of a cell, organ or organism is called as ________.
_________ indudes all the changes that an organism undergoes during its life cycle, from seed germination to senescence.
Read the following statements regarding arithmetic growth and select the correct answer.
(i) Rate of growth is constant.
(ii) One daughter cell remains meristematic while the other one differentiates and matures.
(iii) Mathematical expression is Lt =L0 +rt.
(i) Rate of growth is constant.
(ii) One daughter cell remains meristematic while the other one differentiates and matures.
(iii) Mathematical expression is Lt =L0 +rt.
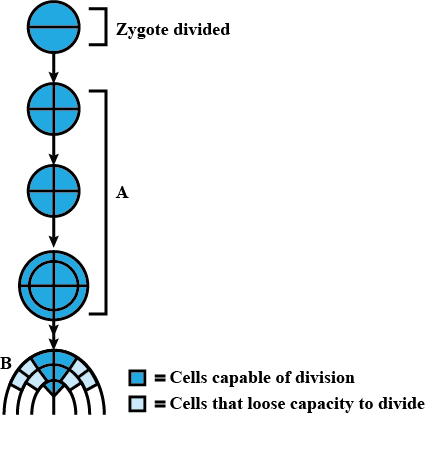
The given figure shows development of an embryo that undergoes two phases A and B. Select the correct option regarding it.
Growth at cellular level, is principally a consequence of increase in the amount of
The given figure shows growth of two leaves over the period of one day. If, AG = absolute growth and RGR = relative growth rate, then select the correct option.

Increase in girth (diameter).of plant as a result of the activities of lateral meristems is called _______________.
Cells of tracheary elements (tracheids and vessels) become dead at maturity and lose their protoplasm due to the deposition of lignocellulosic cell wall thickenings. This is an example of
If a part of pith from the stem of a plant is used as an explant and cultured on nutrient medium, which of the following processes is responsible for the formation of an undifferentiated mass of cells called callus?
Different kinds of structures develop in plants in different phases of growth or in response to environment. This ability is called _________.
Match List - I with List - II.
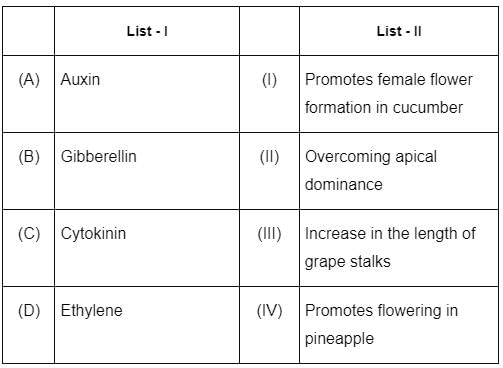
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Plants follow different pathways in response to environment or phases of life to form different kinds of structures. This ability is called:














