Test: Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions (NCERT)
For an ideal solution with pA > pB, which of the following is true? (xA and xB are mole fractions of A and B respectively)
What are the conditions for an ideal solution which obeys Raoult's law over the entire range of concentration?
Intermolecular forces between n-hexane and n-heptane are nearly same as between hexane and heptane individually. When these two are mixed, which of the following is not true about the solution formed?
Which of the following solutions shows positive deviation from Raoult's law?
Which of the following solutions is an example of negative deviation from Raoult's law?
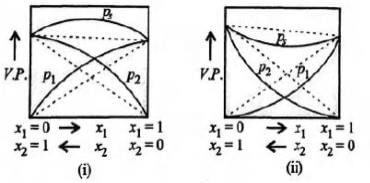
Study the figures given below and mark the correct statement.
When acetone and chloroform are mixed together, hydrogen bonds are formed between them. Which of the following statements is correct about the solution made by mixing acetone and chloroform?
Given below are few mixtures formed by mixing two components. Which of the following binary mixtures will have same composition in liquid and vapour phase?
(i) Ethanol + Chloroform
(ii) Nitric acid + Water
(iii) Benzene + Toluene
(iv) Ethyl chloride + Ethyl bromide
When acetone and chloroform are mixed together, which of the following observations is correct?
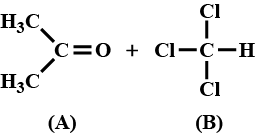
The system that forms maximum boiling azeotrope is



















