Test: Ionic Equilibrium: Acid & Base - NEET MCQ
12 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Ionic Equilibrium: Acid & Base
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-15) This section contains 15 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Which of the following is least likely to behave as Lewis base?
Which of the following is not acid-base conjugate pair?
Which one of the following molecular hydrides acts as a Lewis acid?
The species present in solution when CO2 dissolved in water, are
[IIT JEE 2006]
In the following reaction,
Species behaving as Bronsted-Lowry acids are
Which of the following will produce a buffer solution when mixed in equal volumes ?
Direction Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.
Q. The following thermodynamic quantities are given at 298 K.
Match the parameters given in Column I with their respective values given in Column II.
Codes
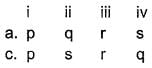
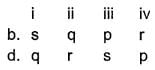
What will be the value of pH of 0.01 mol dm–3 CH3COOH (Ka = 1.74 × 10–5)?
For A- + H2O ⇔ HA + OH-, Kb = 1 x 10-12
Thus, pKa of HA + H2O ⇔ H3O+ + A- is ........