Test: Microbes in Sewage Treatment (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Microbes in Sewage Treatment (NCERT)
The masses of bacteria held together by slime and fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures are called as
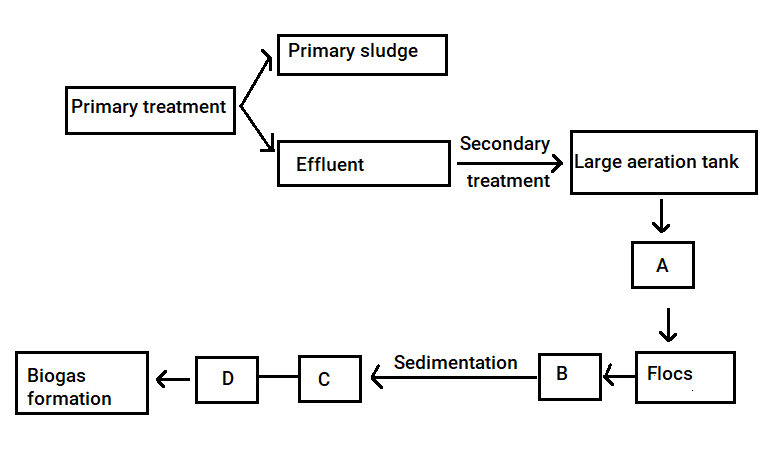
Given below is the flow chart of sewage treatment. Identify A, B, C and D and select the correct option.

Which of the following steps is taken by the Ministry of Environment and Forests to protect rivers from water pollution?
In the sewage treatment, bacterial flocs are allowed to sediment in a setting tank. This sediment is called as
During the primary treatment of sewage, solid particles that settle down are called
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: BOD represents the amount of dissolved oxygen that would be consumed if all the organic matter in one litre of water were oxidised by microorganisms.
Statement 2: High value of BOD indicates that water is highly polluted by organic matter.
____________ is the first step of sewage treatment.
A sewage treatment process in which a part of decomposer bacteria present in the wastes is recycled into the starting of the process is called as:
The purpose of biological treatment of waste water is to
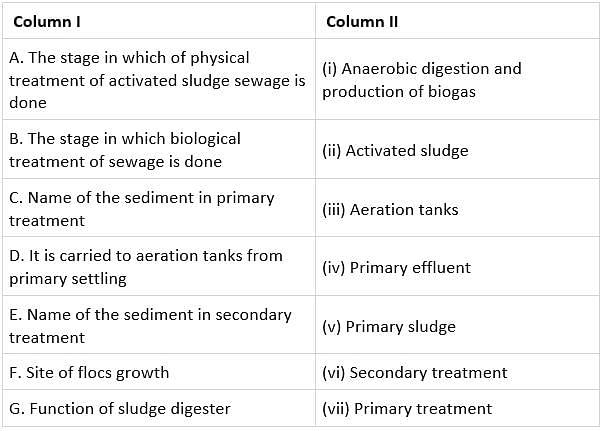
Match column I with column II and select the correct answer from the given codes.
|
78 videos|277 docs|174 tests
|




















