Test: Neural Control & Coordination - 2 - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 11 - Test: Neural Control & Coordination - 2
Which part of the neuron receives incoming signals from other cells?
How do ions contribute to the resting potential of a neuron?
Which neurons transmit impulses towards the central nervous system?
What type of cells are neurons in terms of their membrane potential?
What occurs during the depolarization phase of an action potential?
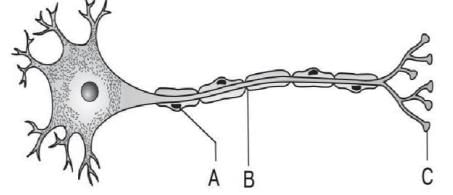
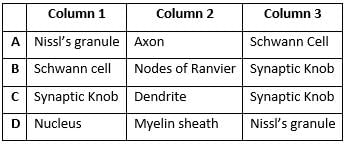
Refer to the given diagram of the structure of a neuron and identify A, B and C.
Assertion: The dendrites of neurons can receive signals from other neurons.
Reason: A multipolar neuron contains numerous axons.
What type of synapse allows for direct flow of electrical signals between neurons?
What is the main function of the autonomic nervous system?
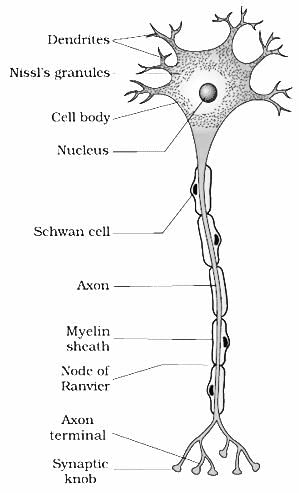
What is the function of Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system?
What establishes the resting potential of a neuron?
What is the role of the limbic system in the brain?
What is the function of the myelin sheath in a myelinated nerve fiber?
What is the main role of the cerebellum in the human brain?
Which part of the human brain is responsible for regulating thirst and hunger?
What is the role of neurotransmitters in a chemical synapse?
Five events in the transmission of nerve impulse across the synapse are given–
A. Opening of specific ion channels allows the entry of ions, a new action potential is generated in the post synaptic neuron.
B. Neurotransmitter binds to the receptor on post synaptic membrane
C. Synaptic vesicle fuses with pre-synaptic membrane, neurotransmitter releases into synaptic cleft
D. Depolarization of pre-synaptic membrane
E. Arrival of action potential at axon terminal.
In which sequence do these events occur?
Which structure connects the two hemispheres of the cerebrum?
Which brain structure is responsible for processing visual and auditory information?
|
180 videos|362 docs|148 tests
|