Test: Organisms & Populations - 1 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Organisms & Populations - 1
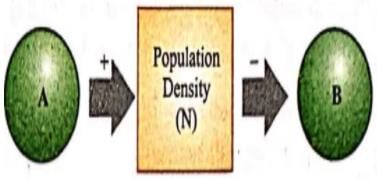
The density of a population in a given habitat during a given period, fluctuates due to changes in certain basic processes. On this basis, fill up boxes A and B in the given flow chart with correct option.

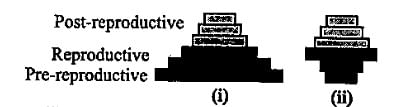
What does the shape of the given age pyramids reflects about the growth status of the related population?

In a pond, last year there were 30 lotus plants. Through reproduction, 25 new lotus plants were added in one year while 8 plants died. The birth and death rates for the lotus population respectively are ___ and ____ individuals per lotus per year.
Which of the following is not an example of using relative density to measure population density in a certain area?
Total number of individuals of a species per unit area and per unit time is called:
Percentage of individuals of a given age group in a given population is called as
In a given population of 2000 individuals, 80 births and 125 deaths were reported over a given period of time. Which of the following graphs will correspond to it?
Which of the following factors has a negative effect on the population growth rate?
If N population density at time t, then population density at time t+1 can be written as
Nt +1=Nt +[(A+B)−(C+D)]
Select the correct option for A, B, C and D in the above equation.
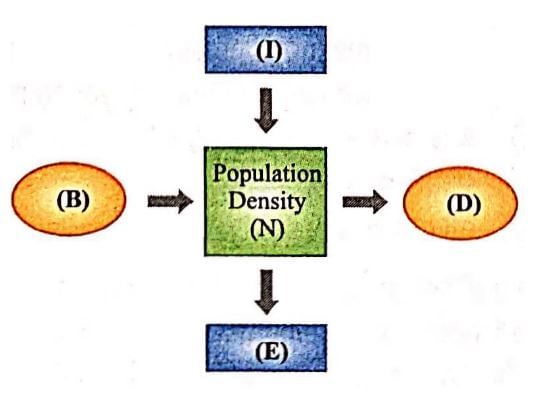
The given figure represents different factors affecting population density (N) If B = nasality, D = mortality, E = emigration and I = immigration; then select the incorrect option regarding these.
Exponential growth is observed in a population when
In a population per capita birth rate is 0.15 and per capita death rate is 0.08 during a unit time period. What is the value of r (intrinsic rate of natural increase) for the given population?
The maximum possible number of individuals that a habitat can support is called its
Which of the following equations correctly represents verhulst-Pearl logistic growth?
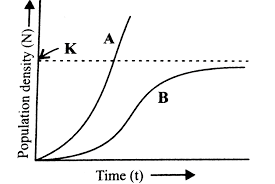
Study the population growth curves (A and B) in the given graph and select the incorrect option
In a life table, the number of individuals alive at the beginning of the 1 st year to 2 nd year interval is 800. During this interval, 200 individuals die. The death rate for this interval is
In a laboratory population of fruit flies, if 4 individuals died during a specified time interval and the population had 40 fruit flies, what is the death rate?
An age pyramid with a wide base and narrow top indicates a population that is:
Interacting members of species live close to each other in following interaction/s:
For which of the following would you expect distribution range to be badly affected if average Global temperature keeps increasing:
Ecology is the study of the relationships between living organisms and:
Which type of interaction benefits both species involved?
Which principle states that the superior competitor eliminates the inferior one in competition?
Exponential growth pattern in a population results into:
In which of the following interaction/s one species is benefitted while other is harmed?
Which growth pattern occurs when resources become progressively limiting in a population?
The birth rate if 7 new plants are added to previous year plant population of 23 Salvinia plants will be:






















