Test: Photoperiodism (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Photoperiodism (Old NCERT)
The plant which requires an exposure to light for a period greater than critical day length is
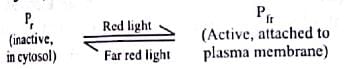
Which of the following is correct about phytochrome?
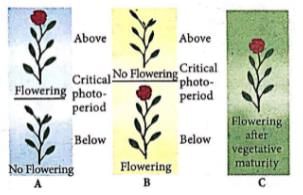
The given figure shows flowering responses of three plants A, B and C to the photoperiod. Select the correct option regarding this.
Maryland mammoth tobacco is a short day plant. Its critical duration of darkness is 10 hours. Under which of the following conditions will it not flower?
Sedum is a long day plant. Its critical duration of light is 13 hours Under which of the following conditions would it flower?

Four potted plants (I, II, Ill, and IV) of a short day plant, which has the critical period of 14 hours; are taken and exposed to light for different time periods. The light periods given are listed in the table.
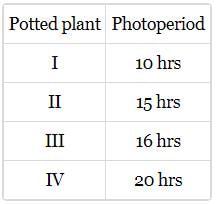
Which potted plant will show flowering after exposure to light?
Low temperature treatment to speed up the process of flowering is referred to as
Cabbage is a biennial plant which produces flowers in the second year of growth. In an attempt to make it flower in a single year, four potted plants (I, II, III, and IV) of cabbage were subjected to different temperatures for several days given in the table.
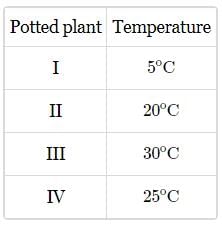
Which potted plant will show flowering?