Test: Population Explosion & Birth Control (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Population Explosion & Birth Control (NCERT)
What is the figure given below showing in particular?
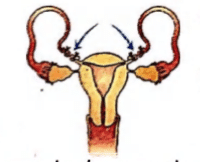

Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Diaphragms, cervical caps and vaults are made of rubber and are inserted into the female reproductive tract to cover the cervix before coitus.
Statement 2: They are chemical barriers of conception and are reusable.
Statement 1: Diaphragms, cervical caps and vaults are made of rubber and are inserted into the female reproductive tract to cover the cervix before coitus.
Statement 2: They are chemical barriers of conception and are reusable.
Choose the correct answer among the alternatives given :
Which of the following contraceptive methods correctly matches with its mode of action?
Which of the following contraceptive methods correctly matches with its mode of action?
CuT is an intrauterine contraceptive device. Select the option that correctly defines the role of Cu
Which of the following statements about Intra Uterine Devices (IUDs) is correct?
Which of the following are the reasons for population explosion?
(i) Increased health facilities
(ii) Rapid increase in MMR
(iii) Rapid increase in IMR
(iv) Rapid decrease in MMR
(v) Decrease in number of people reaching reproductive age
Fill up the blanks in the following paragraph by selecting the correct option.
A. ______(i) methods work on the principle of avoiding chances of ovum and sperms meeting.
B. ______(ii) is one such method in which the couples avoid coitus from day 10 to 17 of the menstrual cycle.
C. ______(iii) is another method in which the male partner withdraws his penis from the vagina just before ejaculation so as to avoid insemination.
D. ______(iv) method is based on the fact that ovulation and therefore the cycle do not occur during the period of intense lactation following parturition.
Which of the following contraceptive methods has poor reversibility?
Which of the following is not a characteristic of an ideal contraceptive?
How do the pills work?
(i) Inhibit ovulation and implantation
(ii) Alter the quality of cervical mucus to prevent or retard the entry of sperms
(iii) Prevent the ejaculated semen from entering the female vagina
(iv) Inhibit spermatogenesis
Progesterone pill helps in preventing pregnancy by not allowing
On which of the following facts does the method of periodic abstinence is based?
Which of the following contraceptives are implanted under the skin?
Which of the following statements are correct regarding surgical methods of contraception?
(i) These are generally advised to the male/female partner as a terminal method to prevent any more pregnancies.
(ii) Surgical procedure in male is called tubectomy and that in the female,vasectomy.
(iii) Reversibility is easily possible.
(iv) They block gamete transport and thereby prevent conception.
The best way to decrease population of a country is
Read the given statement and select the correct option
Statement 1: Saheli is an pill which has high contraceptive value and very little side effects
Statement 2: It contains progestin with no estrogen, and a non-steroidal preparation called centchroman.
What is true for lactational amenorrhea?
(i) It means absence of menstruation.
(ii) Ovulation does not occur during the lactational period.
(iii) Chances of contraception are almost nil upto six months following parturition.
(iv) Side effects are almost nil
(v) Contraceptive efficiency reduces after the period of intense lactation.
(vi) It is a natural method of contraception.
(vii) It increases phagocytosis of sperms.
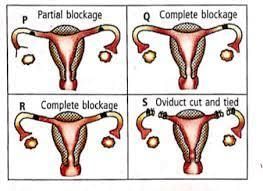
The accompanying diagram shows the uterine tubes of four women (P, Q, R and S). In which two women is fertilisation impossible at present?
Read the given statements and select the correct option
Statement 1: The world population was around 2 billions in 1900 which has rocketed to about 6 billions by 2000
Statement 2: Increase in longevity due to decline in death rate, maternal mortality rate and infant mortality rate has been some major causes of population explosion.
The birth control device used by women is /are
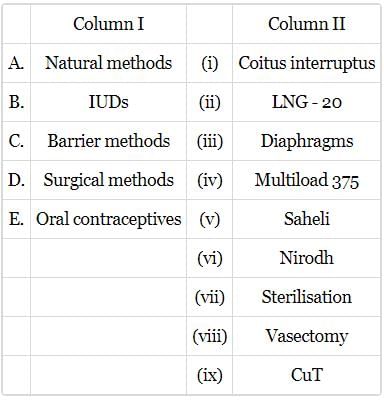
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
Read the following statements and select the option having both incorrect statements.
(i) Condoms decrease sperm motility.
(ii) Diaphragms, cervical caps and vaults are for both males and females.
(iii) IUDs are inserted by-expert nurses.
(iv) Sterilisation is a terminal method to prevent further pregnancy.
(a) Is a natural method of contraception
(b) Is similar to LNG-20 in its mechanism of action
(c) Can be self-inserted by males
(d) Is a barrier method of contraception
|
78 videos|277 docs|174 tests
|





















