NEET Exam > NEET Tests > Biology Class 12 > Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT)
Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) for NEET 2025 is part of Biology Class 12 preparation. The Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) questions and answers have been
prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus.The Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) below.
Solutions of Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) questions in English are available as part of our Biology Class 12 for NEET & Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) solutions in
Hindi for Biology Class 12 course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) | 10 questions in 10 minutes | Mock test for NEET preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Biology Class 12 for NEET Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 1
Plasmid used to construct the first recombinant DNA was isolated from which bacterium species?
Detailed Solution for Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 1
Detailed Solution for Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 2
Detailed Solution for Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 3
Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 4
Which of the following statement is not correct?
Detailed Solution for Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 4
Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 5
Who is the father of genetic engineering?
Detailed Solution for Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 5
Detailed Solution for Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 6
Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 7
One of the key factors, which makes the plasmid the vector in genetic engineering is
Detailed Solution for Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 7
Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 8
Genetic engineering is possible, because
Detailed Solution for Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 8
Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 9
Which of the following processes/techniques can be included under biotechnology?
(i) In vitro fertilisation
(ii) Synthesis of a gene
(iii) Correcting a defective gene
(iv) Developing a DNA vaccine
Detailed Solution for Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 9
Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 10
Match the scientists in column I with their related discoveries in column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
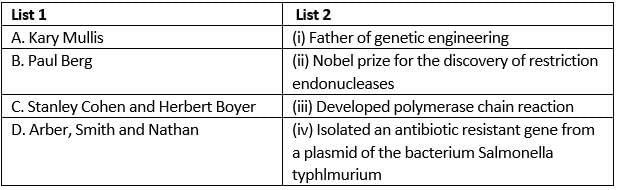
Detailed Solution for Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) - Question 10
|
78 videos|277 docs|174 tests
|
Information about Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Principles of Biotechnology (NCERT), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice




















