Test: Processes of Recombinant DNA Technology (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Processes of Recombinant DNA Technology (NCERT)
Stirred-tank bioreactors have advantages over shake flasks because they ___________.
The different steps of recombinant DNA technology are given below randomly.
(i) Isolation of the DNA fragments or genes to be cloned
(ii) Introduction of the recombinant DNA into a suitable cell (usually E.coli) called host (transformation)
(iii) Multiplication/expression of the introduced gene in the host
(iv) Selection of the transformed host cells, and identification of the clone containing the desired gene/DNA fragment
(v) Insertion of the isolated gene in a suitable plasmid vector
Which of the following represents the correct sequence of steps?
(i) Isolation of the DNA fragments or genes to be cloned
(ii) Introduction of the recombinant DNA into a suitable cell (usually E.coli) called host (transformation)
(iii) Multiplication/expression of the introduced gene in the host
(iv) Selection of the transformed host cells, and identification of the clone containing the desired gene/DNA fragment
(v) Insertion of the isolated gene in a suitable plasmid vector
Given table gives an account of differences between PCR and gene cloning.. Which of the following points show the incorrect differences?


Enzyme' Taq polymerase' used in PCR, has been isolated from bacterium ________.
In addition to the Taq polymerase enzyme, which other thermostable DNA polymerases have been isolated to be used in a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)?
After completion of the biosynthetic stage in the bioreactors, the product undergoes separation and purification processes, collectively termed as __________.
During isolation of genetic material, the chemical used to precipitate out the purified DNA is
The given flow chart depicts the steps to transfer a desirable gene of interest into a plant.
Identify the missing steps (A, B and C) with regard to following statements and select the correct option.
(i) Joining of desirable gene to a suitable cloning vector using ligases to create a recombinant DNA molecule
(ii) Selection of transformed cells
(iii) Transferring the recombinant DNA molecules to the target cells
Eukaryotic genes do not function properly when cloned into a bacterial cell because
Match column I with column II and select the correct answer from the given codes.
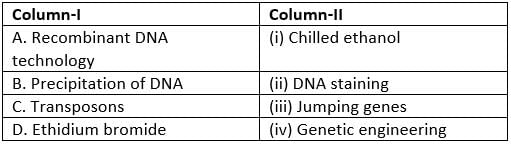
Study the following statements regarding recombinant DNA technology and select the incorrect ones
(i) Taq polymerase extends the primers using the nucleotides provided in the reaction
(ii) Antibiotic resistance genes are considered as desirable genes in recombinant DNA technology
(iii) DNA fragments are separated according to their charge only, in agarose gel electrophoresis
(iv) Transformation is a procedure through which a piece of DNA is integrated into the genome of a host bacterium
(v) To produce higher yields of the desired protein, host cells can be multiplied in a continuous culture
(vi) Downstream processing is one of the steps of polymerase chain reaction
Which of the following are the types of bioreactors?
(i) Simple stirred-tank bioreactor
(ii) Complex Stirred-tank bioreactor
(iii) Sparged stirred-tank bioreactor
(iv) Agitator stirred-tank bioreactor
Read statements (i)-(iv). Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Restriction enzymes belong to a larger class of enzymes called nucleases.
(ii) Restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA at specific sites.
(iii) Downstream processing is one of the steps of rDNA technology.
(iv) Disarmed pathogen vectors are also used in the transfer of rDNA into the host.
An advantage of using yeasts rather than bacteria as recipient cells for the recombinant DNA of eukaryotes is that yeasts can __________.
|
78 videos|277 docs|174 tests
|




















