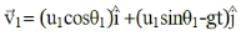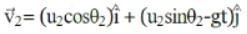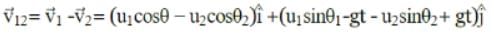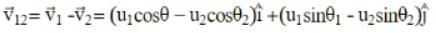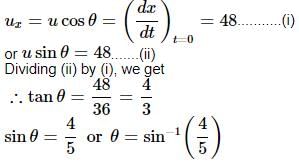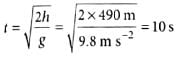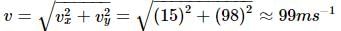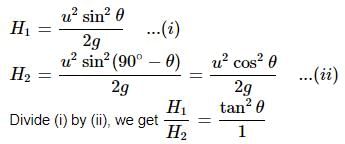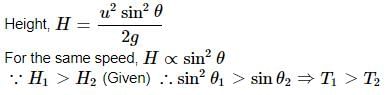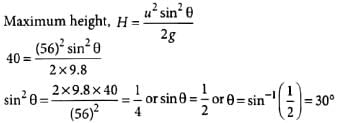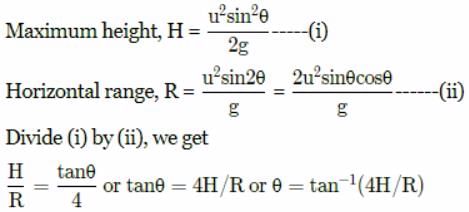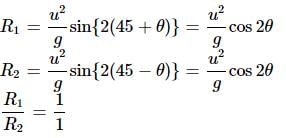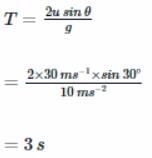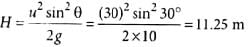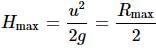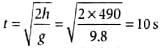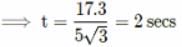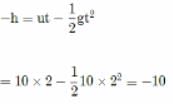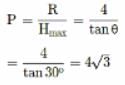Test: Projectile Motion (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Projectile Motion (NCERT)
Which of the following is true regarding projectile motion?
A bomb is released by a horizontal flying aeroplane. The trajectory of the bomb is
In case of a projectile motion, what is the angle between the velocity and acceleration at the highest point?
If a body is projected with an angle θ to the horizontal, then
Two particles are projected simultaneously in the same vertical plane, from the same point, both with different speeds and at different angles with horizontal. The path followed by one, as seen by the other, is
A football is kicked into the air vertically upwards with velocity u. The velocity of the ball at the highest point is
The equations of motion of a projectile are given by x = 36t m and 2y = 96t - 9.8t2 m. The angle of projection is
The relation between the time of flight of projectile Tf, and the time to reach the maximum height tm is
A hiker stands on the edge of a cliff 490 m above the ground and throws a stone horizontally with a speed of 15 m s-1. The time taken by the stone to reach the ground is
The speed with which the stone hits the ground is
Two balls are projected at an angle θ and (90° - θ) to the horizontal with the same speed. The ratio of their maximum vertical heights is
Two particles are projected in air with speed u at angles θ1 and θ2 (both acute) to the horizontal, respectively. If the height reached by the first particle is greater than that of the second, then which one of the following is correct?
(where T1 and T2 are the time of flight.)
The ceiling of a hall is 40 m high. For maximum horizontal distance, the angle at which the ball may be thrown with a speed of 56 m s-1 without hitting the ceiling of the hall is
The maximum horizontal distance covered by the ball will be
If R and H represent horizontal range and maximum height of the projectile, then the angle of projection with the horizontal is:
When air resistance is taken into account while dealing with the motion of the projectile which of the following properties of the projectile, shows an increase?
Two projectiles are are fired from the same point with the same speed at angles 60° and 30° respectively. Which one of the follwing is true?
Galileo writes that for angles of projection of a projectile at angle (45o + θ) and (45o − θ), the horizontal ranges described by the projectile are in the ratio of: (if θ ≤ 45o)
A cricket ball is thrown at a speed of 30ms−1 in a direction 30∘ above the horizontal. The time taken by the ball to return to the same level is
(Take g = 10ms−2)
A cricket ball is thrown at a speed of 30ms−1 in a direction 30∘ above the horizontal. Then the distance from the thrower to the point where the ball returns to the same level is
A cricket ball is thrown at a speed of 30ms−1 in a direction 30∘ above the horizontal. The maximum height attained by the ball is
A cricketer can throw a ball to a maximum horizontal distance of 100m. With the same speed how much high above the ground can the cricketer throw the same ball?
An aeroplane flying horizontally with a speed of 360 km h-1 releases a bomb at a height of 490 m from the ground. If g = 9.8 m s-2, it will strike the ground at
A ball is thrown from the top of a tower with an initial velocity of 10 m s-1 at an angle ot 30° with the horizontal. If it hits the ground at a distance of 17.3 m from the base of the tower, the height of the tower is (Take g = 10 m s-2)
The speed of a projectile at its maximum height is √3/2 times its initial speed. If the range of the projectile is P times the maximum height attained by it, then P equals



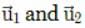 be the initial velocities of the two particles and θ1 and θ2 be their angles of projection with the horizontal.
be the initial velocities of the two particles and θ1 and θ2 be their angles of projection with the horizontal.