Test: Secondary Growth (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Secondary Growth (NCERT)
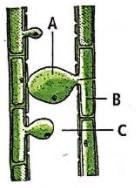
Identify the given figure and select the correct labels for A, B and C.


In dicot stems, cambium present between primary xylem and primary phloem is
Which of the following statements is correct about a woody dicot stem which shows extensive secondary growth?
In old trees, central dark coloured, non-conducting part of secondary xylem is referred to as
Which of the following options correctly shows the sequence of different tissues of the periderm starting from periphery?
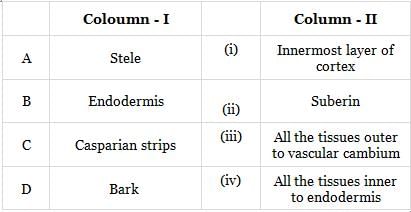
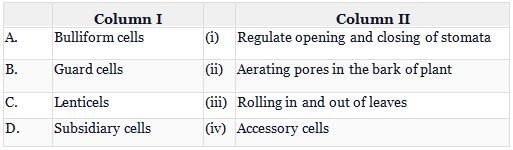
Match Column-I with Column-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Match Column-I with Column-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below.
During the secondary growth in a dicotyledonous stem, the fusiform initials of vascular cambium give rise to
Cork is impervious to water due to the presence of _______ in its cell wall.
Bark formed early in the season is called as________ bark and bark formed towards the end of the season is called as _________bark.
During secondary growth in a dicot root, cork cambium is formed by the activity of
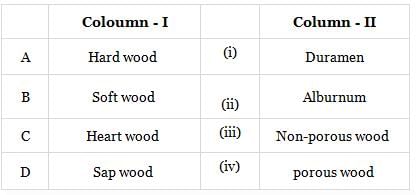
Match Column-I with Column-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Bark of which of the following plants yields a drug for the treatment of malaria?
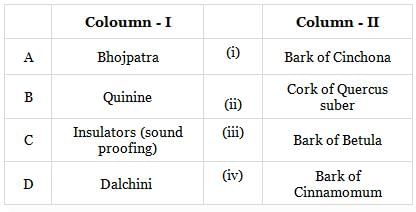
Match Column-I with Column-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below.