Test: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - 4 - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Test: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - 4
In albuminous seeds, food is stored in _______ and in non albuminous seeds, it is stored in _______.
In the given diagram showing the structure of a monocot seed:
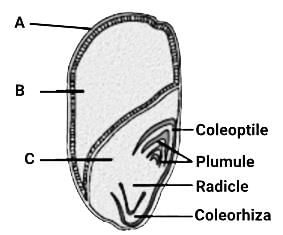
Statement I:A is pericarp.
Statement II:B is the cotyledon of the monocot seed.
Statement III: C is triploid in nature and develops before B.

Statement II:B is the cotyledon of the monocot seed.
Statement III: C is triploid in nature and develops before B.
In an embryo sac, the cells that degenerate after fertilisation are
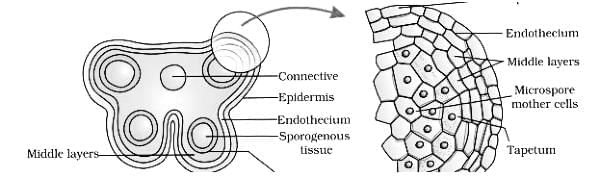
The anther wall consists of four wall layers where
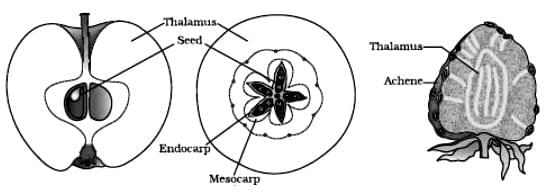
The diagram shows the false fruits of apple and strawberry.
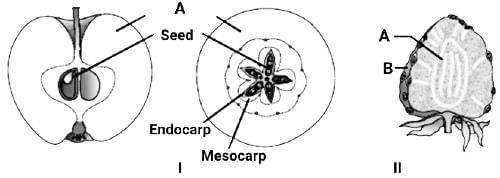
Statement I: False fruits develop only from the ovary.
Statement II: A is Thalamus and B is Achene.
Assertion a: All the fruits that we eat are not real fruits.
Reason (R): In a few plants, floral parts like thalamus or pedicel also contribute to fruit formation. Such fruits are called false fruits.
Number of seeds are equal to the
Assertion : Endosperm is a nutritive tissue and it is triploid.
Reason : Endosperm is formed by fusion of secondary nucleus to second male gamete. It is used by developing embryo.
Which one of the following statements is correct?
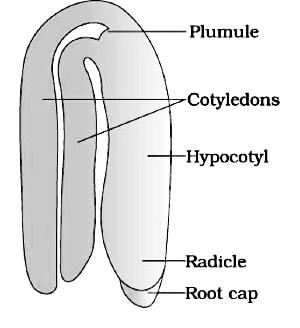
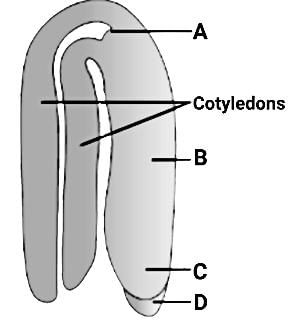
identify A- D in the diagram showing a typical dicot embryo:
Which one of the following statements regarding post-fertilisation development in flowering plants is incorrect?
The following figure represents :
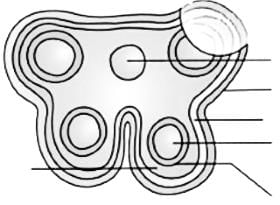
|
9 docs|1256 tests
|