NEET Exam > NEET Tests > NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions > Test: The Seed (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
Test: The Seed (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
Test Description
5 Questions MCQ Test NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions - Test: The Seed (NCERT)
Test: The Seed (NCERT) for NEET 2025 is part of NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions preparation. The Test: The Seed (NCERT) questions and answers have been
prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus.The Test: The Seed (NCERT) MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: The Seed (NCERT) below.
Solutions of Test: The Seed (NCERT) questions in English are available as part of our NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions for NEET & Test: The Seed (NCERT) solutions in
Hindi for NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: The Seed (NCERT) | 5 questions in 5 minutes | Mock test for NEET preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions for NEET Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: The Seed (NCERT) - Question 1
Monocotyledonous seeds possess a single cotyledon which is represented by
Detailed Solution for Test: The Seed (NCERT) - Question 1
Test: The Seed (NCERT) - Question 2
Coleorhiza and coleoptile are the protective sheaths covening _____ and _____ respectively.
Detailed Solution for Test: The Seed (NCERT) - Question 2
Detailed Solution for Test: The Seed (NCERT) - Question 3
Test: The Seed (NCERT) - Question 4
Identify A, B, C and D in the given figure showing L.S. of a monocot seed and select the correct option.
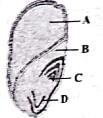
Detailed Solution for Test: The Seed (NCERT) - Question 4
Test: The Seed (NCERT) - Question 5
Which of the following statements correctly describes the structure of a seed?
Detailed Solution for Test: The Seed (NCERT) - Question 5
|
257 docs|234 tests
|
Information about Test: The Seed (NCERT) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: The Seed (NCERT) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: The Seed (NCERT), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice




















