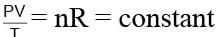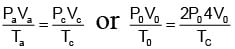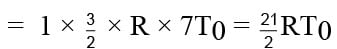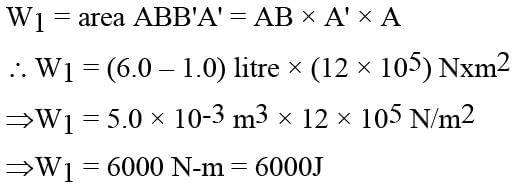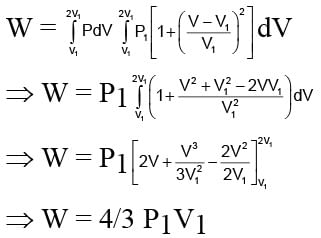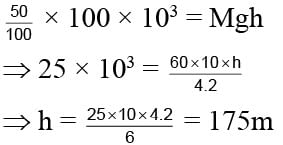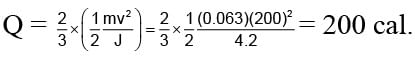Test: Thermodynamic Processes - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Thermodynamic Processes
Heat is supplied to the gas, but its internal energy does not increase. What is the process involved?
Find the final temperature of one mole of an ideal gas at an initial temperature to t K.The gas does 9 R joules of work adiabatically. The ratio of specific heats of this gas at constant pressure and at constant volume is 4/3.
Two gases X and Y kept in separate cylinders with same initial temperature and pressure are compressed to one third of their volume through isothermal and adiabatic process respectively. Which gas would have more pressure?
An adiabatic change in represented by the equation –
Isothermal process can be represented by which law?
The internal energy of monatomic and diatomic gases are respectively due to
Calculate the work done by the gas in an isothermal process from A to B. PA = 1Pa, VA = 3m3, PB = 3Pa.
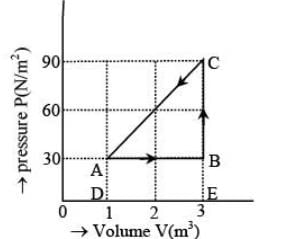
In the figure (A) indicator diagram, the net amount of work done will be :
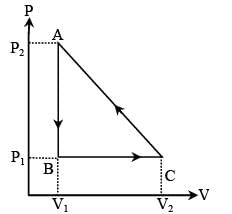
In the figure (A) the work done by the system in the closed path ABCA is
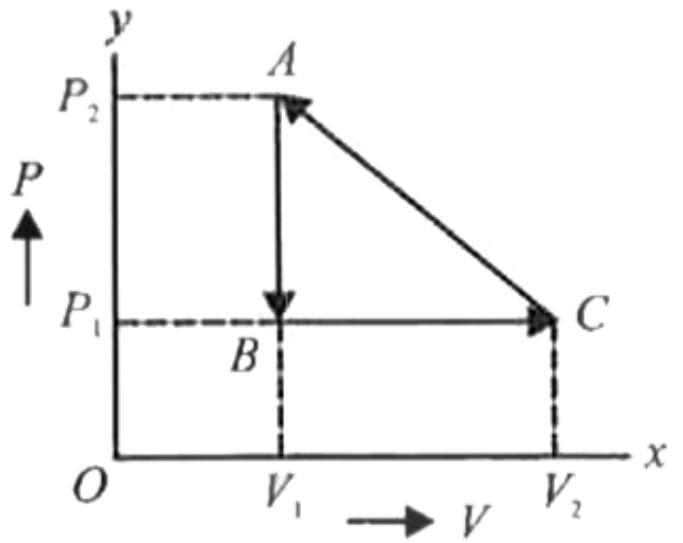
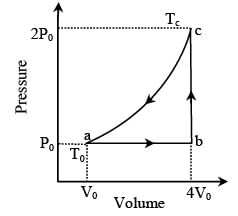
One mole of an ideal monatomic gas is caused to go through the cycle shown in fig. then the change in the internal energy in expanding the gas from a to c along path abc is
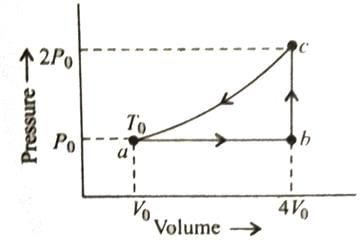
The diagram shows a P-V graph of the thermodynamic behavior of an ideal gas. Find to this graph work done in processes A → B, B → C, C → D and D → A

The figure shows the change in a thermodynamic system is going from an initial state A to the state B and C and returning to the state A. if UA = 0, UB = 30J an the heat given to the system in the process B → C, 50J, then determine:
(i) internal energy in the state C
(ii) heat given to the system in the process A B
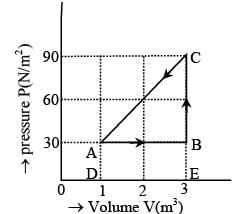
The figure shows the change in a thermodynamic system is going from an initial state A to the state B and C and returning to the state A. if UA = 0, UB = 30J an the heat given to the system in the process B → C, 50J, then find out heat given to the system or taken out from the system in the process C → A and network done in complete cycle.
An ideal gas expands from state (P1, V1) to state (P2, V2) where P2 = 2P1 and V2 = 2V1. The path of the gas is expressed by the following relation 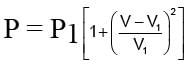 work done is
work done is
For what value is the Fahrenheit temperature equal to the Celsius temperature?
Water fall from a height 50m. If one third its mechanical energy converted into heat what will be the rise in temperature of water.
A man got 100 Kcal heat from its lunch. Its efficiency is only 25% and mass of man is 60 kg. Calculate the height he can acquire.
A 63 gm bullet moving velocity 200 m/s. Collides against a wall consequently two third of it's kinetic energy is converted into heat. Than what will be the heat developed by bullet in calorie. (Given: J = 4.2)
A body of mass 2kg is dragged on a horizontal surface with a constant speed of 2 m/s. If the coefficient of friction between the body and the surface is 0.2, then find the heat generated in 5 sec.