Test: Thermodynamics of Electrochemistry - JEE MCQ
24 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Thermodynamics of Electrochemistry
Only One Option Correct Type
This section contains 15 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
Q.
Temperature coefficient of EMF of a cell in terms of entropy change is
The standard reduction potential at 298 K of the reaction,
2H2O + 2e-  H2 + 2OH- is 0.8277 V
H2 + 2OH- is 0.8277 V
Thus,thermodynamic equilibrium constant for the reaction.
2H2O  H3O+ + OH- at 298 K is
H3O+ + OH- at 298 K is
 H2 + 2OH- is 0.8277 V
H2 + 2OH- is 0.8277 V H3O+ + OH- at 298 K is
H3O+ + OH- at 298 K is Given ,
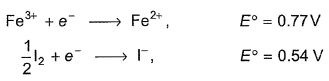
Thus ,equilibrium constant for the reaction in terms of log k is
2Fe3+ + 3I-  2Fe2+ + I-3
2Fe2+ + I-3
 2Fe2+ + I-3
2Fe2+ + I-3 Given ,
Thus ,(log Keq) for the reaction Cu2+ +In2+  Cu+ + In3+ is
Cu+ + In3+ is
An excess of liquid mercury is added to an acidified solution of 1.0 x 10-3 M Fe3+ .Thus is if 5% of Fe3+ remains at equilibrium at 298 K
EMF of the following cell is 0.2905 V
Zn/Zn2+ (a = 0.1M)|| Fe2+ (a = 0.01M)| Fe
The equilibrium constant for the cell reaction is
[IIT JEE 2004]
The half-cell reactions for rusting of iron are
ΔG° (in kJ) for the reaction is
[IIT JEE 2005]
The Gibbs free energy for the decomposition of Al2O3 at 800 K is as follows :
2Al2O3 → 4Al + 3O2 , ΔrG = 2898kJ mol-1
The potential difference needed for electrolytic reduction of Al2O3 is at least
Given ,
The value of standard electrode potential for the half-reaction is
Fe3+(aq) + e- → Fe2+(aq)
For the reaction, 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l), E0cell = 1.23 V at 298 K
and ΔH0f (H2O) = - 285.8 kJ mol-1 Thus, ΔS° (standard entropy change ) is
For the reaction ,
Thus , for the reaction
Consider the following equations for a cell reaction.
A+B  C+ D, E0 = x volt, Keq = K1
C+ D, E0 = x volt, Keq = K1
2A +2B  2C+ 2D, E0 = y volt, Keq = K2
2C+ 2D, E0 = y volt, Keq = K2
Then,
Which of the following statements about the spontaneous reaction occurring in a galvanic cell is always true?
For a (Ag-Zn) button cell ,the net reaction is
Zn(s) + Ag2O(s) → ZnO(s) + 2Ag(s)
ΔG0f(Ag2O) = -11.21kJmol-1, ΔG0 f(ZnO) = - 318.3 kJ mol-1
Hence, E°cell of the button cell is
Matching List Type
Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct
Q.
The standard reduction potential data at 298 K is given below:
Match E° of a redox pair in Column I with the values given in Column II and select the corect answer using the codes given below:
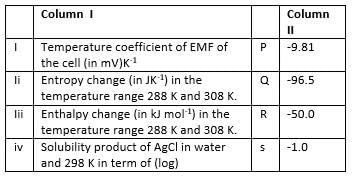
The standard potential of the following cell is 0.23 V at 288 K and 0.21 V at 308 K.
Match the parameters in Column I with their values in Column II and select the answer from the codes given below the list.
Comprehension Type
This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Passage I
The concentration of potassium ions inside a biological cell is at least twenty times higher than the outside. The resulting potential difference across the cell is important in several process such as transmission of nerve impulses and maintaining the ion balance. A simple model for such a concentration cell involving a metal M is
M(s) | M+ (aq, 0.05M), || M+(aq) 1M|M(s) | Ecell | = 77mV
Q.
For the above cell,
Passage I
The concentration of potassium ions inside a biological cell is at least twenty times higher than the outside. The resulting potential difference across the cell is important in several process such as transmission of nerve impulses and maintaining the ion balance. A simple model for such a concentration cell involving a metal M is
M(s) | M+ (aq, 0.05M), || M+(aq) 1M|M(s) | Ecell | = 77mV
Q.
If 0.05 M solution of M+ is replaced by 0.0025 M solution of M+,then |Ecell | would be
Passage II
Given,
ΔG0f(AgCl) = -109kJmol-1, ΔG0f(Cl-) = -129kJmol-1
ΔG0f(Ag+) = 77kJmol-1,
Thus E°cell of the cell reaction is
Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) → AgCl(s) is
Passage II
Given,
ΔG0f(AgCl) = -109kJmol-1, ΔG0f(Cl-) = -129kJmol-1
ΔG0f(Ag+) = 77kJmol-1,
Q.
Ksp of AgCl is thus,
One Integer Value Correct Type
This section contains 3 questions, when worked out will result in an integer value from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q.
A platinum electrode is immersed in a solution containing 0.1 M Fe2+ and 0.1 M Fe3+.It iscoupled with SHE.Concentration Fe3+ of increased to 0.1 M without change in [Fe2+], then the change in EMF (in centivolt) is
Using Cr2O72- aqueous, solution
E0red = 1.33V and ΔG0 = -770.07 kJmol-1
What is the valency of the ion formed after reduction?
Equilibriumconstant of the cell reaction,
Cu + 2Fe3+  2Fe2+ + cu2+ is y x 1014
2Fe2+ + cu2+ is y x 1014
What is the value of y?



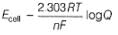
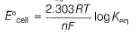
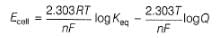
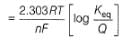


 Ag+ + Cl- E0 = -0.59V
Ag+ + Cl- E0 = -0.59V











