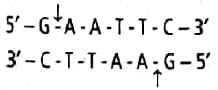Test: Tools of Recombinant DNA Technology (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Tools of Recombinant DNA Technology (NCERT)
The restriction enzyme responsible for the cleavage of following sequence is
5' - G - T - C - G - A - c - 3'
3' - C - A - G - C - T - G - 5'
5' - G - T - C - G - A - c - 3'
3' - C - A - G - C - T - G - 5'
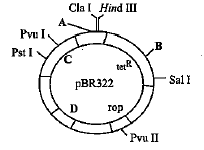
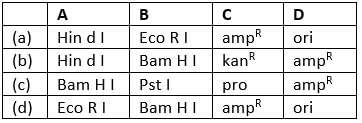
Identify A, B, C and D in the given figure of E. coli cloning vector pBR322 and select the correct option

Read the following statements and select the correct ones.
(i) Electrophoresis is a technique used for the separation of molecules based on their size and charge
(ii) Plasmids are extra-chromosomal, self-replicating, usually circular, double-stranded DNA molecules found naturally in many bacteria and also in some yeast
(iii) It is not advisable to use an exonuclease enzyme while producing a recombinant DNA molecule
(iv) In EcoRI, the roman numeral I indicates that it was the first enzyme isolated from E.coli RY 13
(i) Electrophoresis is a technique used for the separation of molecules based on their size and charge
(ii) Plasmids are extra-chromosomal, self-replicating, usually circular, double-stranded DNA molecules found naturally in many bacteria and also in some yeast
(iii) It is not advisable to use an exonuclease enzyme while producing a recombinant DNA molecule
(iv) In EcoRI, the roman numeral I indicates that it was the first enzyme isolated from E.coli RY 13
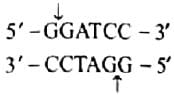
Identify the palindromic sequence in the following.
Which of the following statements is not correct regarding EcoRI restriction endonuclease enzyme?
If a recombinant DNA bearing gene for resistance to antibiotic ampicillin is transferred to E.coli cells, the host cells become transformed into ampicillin-resistant cells. If such bacteria are transferred on agar plates containing ampicillin, only transformants will grow and the non-transformed recipient cells will die. The ampicillin-resistant gene in this case is called as _______.
If you want to recover many copies of the target DNA, you will choose a vector
The flow chart given below represents the process of recombinant DNA technology. Identify A, B, C and D
Which of the following tools of recombinant DNA technology is incorrectly paired with its use?
In recombinant DNA technology, the term vector refers to
The letter 'R' in EcoRI is derived from
How many fragments will be generated if you digest a linear DNA molecule with a restriction enzyme having four recognition sites on the DNA?
In the process of insertional inactivation
How many fragments will be generated on the digestion of a closed circular DNA molecule with a restriction enzyme having six recognition sites on the DNA?
______ a crown gall bacterium, is called as 'natural genetic engineer' of plants.
Which of the following is not used to transfer the recombinant DNA into the host?
Which of the following is required for microinjection method of gene transfer?
In biolistic method of gene transfer, the microparticles coated with foreign DNA are bombarded into target cells at a very high velocity. These microparticles are made up of
Which of the following sequences is recognised by restriction enzyme Bam H I?
Which of the following is not a cloning vector?
Which of the following statements is correct for molecular probes?
What is the effect if pBR322, a cloning vector does not carry 'ori site'?
In pBR322, tetracycline resistance gene (tetR) has recognition site for which of the following restriction endonuclease?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: The tumour inducing plasmid (Ti plasmid) acts as a cloning vector in recombinant DNA technology.
Statements 2: The Ti plasmid which is used in the mechanisms of delivering genes to a cell remains pathogenic.
The sticky ends of a fragmented DNA molecule are made of
Match the terms given in column I with their definitions in column II and select the correct answer from codes given below.

If a plasmid vector is digested with EcoRI at a single site, then
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: The cloning vector is required to have very few, preferably single, recognition sites for the commonly used restriction enzymes.
Statement 2: Presence of more than one recognition sites within a cloning vector will generate several fragments, which will complicate the process of gene cloning.
A correct pair of characteristics of molecular probe is
A. Very long molecule
B. Double stranded
C. Single stranded DNA or RNA
D. Complementary to part of desired gene
|
78 videos|277 docs|174 tests
|



 is a palindromic sequence.
is a palindromic sequence.