Important Questions Test: Fun With Magnets - Class 6 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Important Questions Test: Fun With Magnets
In the given diagrams, compasses are used to plot the magnetic field around a bar magnet with poles marked N (North) and S (South). Which of the following diagrams correctly shows the expected field pattern?
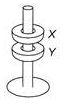
The illustration depicts a ring magnet, X, levitating above another ring magnet, Y. This phenomenon occurs because

Reeta puts two different objects in each of the following containers.
Container (i): Copper coin and iron nail
Container (ii): Iron and wood
Container (iii): Marble and cloth
Container (iv): Nickel coin and paper bits
She can use a magnet to separate the objects in containers
Container (i): Copper coin and iron nail
Container (ii): Iron and wood
Container (iii): Marble and cloth
Container (iv): Nickel coin and paper bits
She can use a magnet to separate the objects in containers
A bar magnet is immersed in a heap of iron filings and pulled out. The amount of iron filing clinging to the
It has a needle, which is itself a magnet. What is it
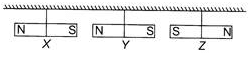
What will happen when three bar magnets are hung in the manner as shown below?
Magnets lose their properties significantly if
A matchbox containing an unknown object is placed on a thin sheet of glass in the experimental set-up shown in the figure.
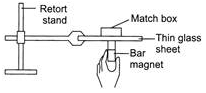
When the bar magnet moves, it is able to drag the match box along. What is most likely to be found in the matchbox?
Which of the following is non-magnetic?
How many combined north and south poles are present in a magnet if it is broken into 6 pieces without loss of magnetism?
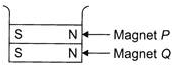
Two magnets are placed in a container as shown in the figure by some external force. What would happen if the force on magnet P is removed?
Materials which are attracted towards a magnet are known by which name?
Which of the following is the best way to keep magnets?
Arun suspended a bar magnet on a string as shown in the diagram below. He brought 3 bar-shaped objects P, Q and R towards the bar magnet. He placed the ends (X and Y) of each object, near the north pole of the bar magnet and recorded his observations in the table below.
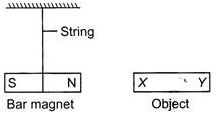
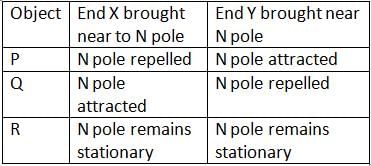
Which of the object(s) is/are the magnet?
What is the North Seeking Pole of a magnet?
Two bar magnets suspended by string, are separated by a piece of metal. Which of the following statements best explain the outcome shown in the diagram?

Observe the given figure and identify the correct statements.

(i) Poles 1, 3 and 5 are unlike poles.
(ii) Poles 2, 4 and 6 are like poles.
(iii) Pole 1 will attract pole 3 and 5.
(iv) Pole 4 will be attracted by pole 1.














