Class 4 Exam > Class 4 Tests > Science Olympiad Class 4 > Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Class 4 MCQ
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Class 4 MCQ
Test Description
20 Questions MCQ Test Science Olympiad Class 4 - Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 for Class 4 2025 is part of Science Olympiad Class 4 preparation. The Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 questions and answers have been
prepared according to the Class 4 exam syllabus.The Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 MCQs are made for Class 4 2025 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 below.
Solutions of Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 questions in English are available as part of our Science Olympiad Class 4 for Class 4 & Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 solutions in
Hindi for Science Olympiad Class 4 course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for Class 4 Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 | 20 questions in 40 minutes | Mock test for Class 4 preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Science Olympiad Class 4 for Class 4 Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 1
Aerial animals are animals that spend most of their time:
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 1
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 2
Camouflage is a kind of adaptation in which an organism deceives others by merging its colour with that of its surroundings. Which of the following colours would best suit a chameleon to hide from its enemies in a forest when it sits on a branch of a tree?
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 2
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 3
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 4
Find the mismatched pair according to animals and their habitats:
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 4
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 5
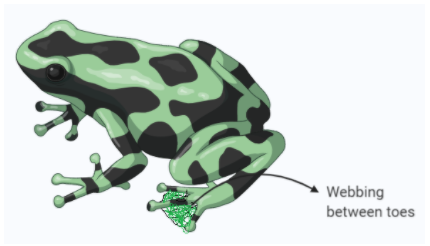
The feet of frogs and ducks are webbed. This adaptation helps them to:
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 5
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 6
Which of the following animals can live on both water and land?
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 6
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 7
A student identifies the following characteristics in an animal:
1. Strong claws and broad hip girdles
2. Spines to prevent slipping
3. Ability to climb trees
Q. Which is the best-suited title for this animal?
1. Strong claws and broad hip girdles
2. Spines to prevent slipping
3. Ability to climb trees
Q. Which is the best-suited title for this animal?
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 7
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 8
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 9
Tigers and leopards have stripes on their bodies. This adaptation helps them to:
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 9
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 10
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 11
What is the primary adaptation mechanism of a chameleon?
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 11
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 12
An animal is taken to the polar region. Which of the following adaptive characteristics will help it to survive in its new environment?
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 12
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 13
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 14
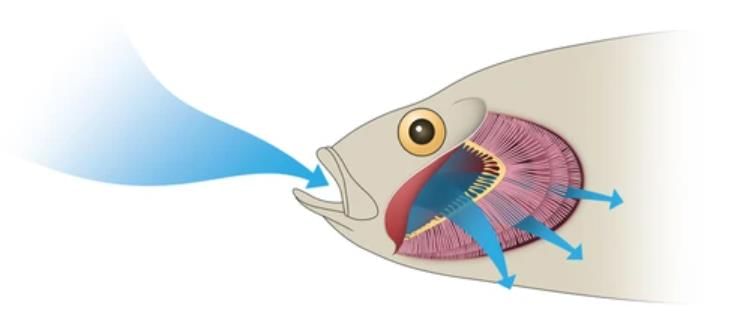
How can fishes survive inside water?
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 14
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 15
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 16
The polar bear is adapted to live in the:
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 16
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 17
Camels are adapted to living for many days without
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 17
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 18
Which of these is adapted to swim?
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 18
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 19
Which of these animals is adapted to live in the desert?
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 19
Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 20
What type of diet does a bear primarily have?
Detailed Solution for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 - Question 20
|
53 videos|44 docs|59 tests
|
Information about Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Olympiad Test: Living And Non-living Things -1, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice