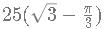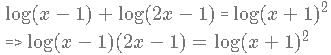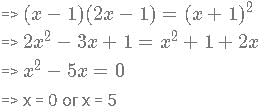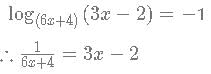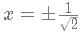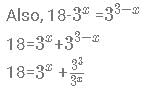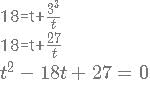Test: CAT Quantitative Aptitude- 1 - CAT MCQ
22 Questions MCQ Test - Test: CAT Quantitative Aptitude- 1
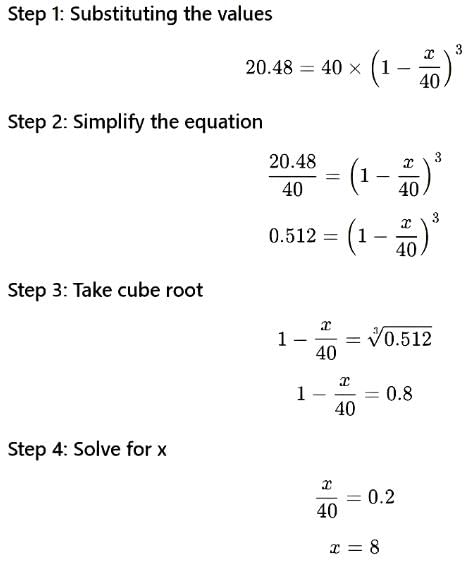
Some milk from a container, having 40 litres of milk, is drawn out and replaced with an equal amount of water. This process is repeated two more times and after that, only 20.48 litres of milk is left in the container. What is the amount of solution (in litres) removed in each iteration?
Eight years ago, the ratio of ages of Akhil and Akash was 1:5. 12 years from now, the ratio changes to 7 : 15. Find the sum of the antecedent and the consequent of the ratio of their present ages, when the ratio is in its lowest form.
Ratnesh bought a fridge and a television from big bazaar. He was promised 20% discount on the fridge and 25% discount on the television. However, a con salesman, interchanged the discount offered on both the items and processed the bill. If the mark price of the television is 4 times that of the fridge, then what is the ratio of the amount actually paid by Ratnesh to that he would have paid if he was not cheated?
Arun, Barun, Chandan and Diksha have books in the ratio 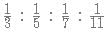 respectively. What is the the minimum number of books they must be having altogether?
respectively. What is the the minimum number of books they must be having altogether?
(Enter ‘0’ as the answer if the answer cannot be determined.)
Given that [(x-y)(1/4)] = 2 and [(3x−2y) 1/2] = 5. What is the minimum possible integral value of y? [x] is equal to greatest integer less than or equal to x.
How many points in the region enclosed by x > 0, y < 0 and 7x - 9y < 63 have integral coordinates?
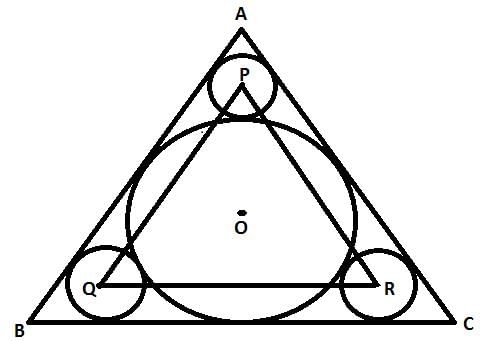
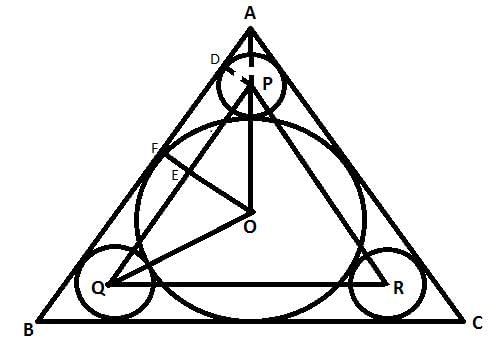
A circle with radius 6 cm is inscribed inside an equilateral triangle ABC. Three smaller circle are drawn touching the incircle and the sides of ABC as shown in the figure. Another triangle is formed by joining centres P,Q and R of these smaller circles. What is the perimeter of triangle PQR?
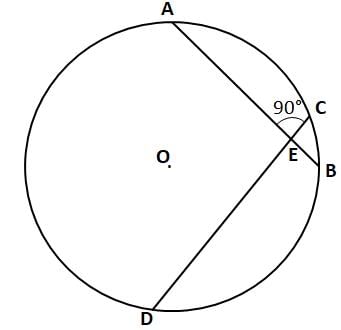
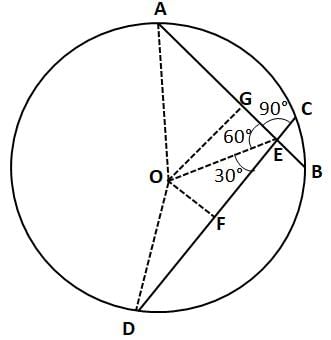
In a circle, two chords AB and CD intersect at a point E as shown in the figure. If AB = 6 cm and CD = 10 cm and ∠ OED = 30°, then find out the radius of the given circle.
How many scalene triangles with integral sides can be formed with a perimeter of 45 cm?
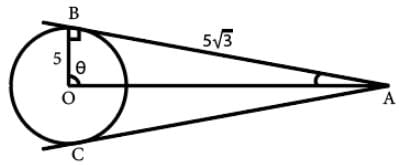
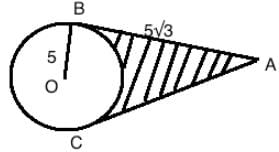
AB and AC are tangents to the circle with centre O. If the radius of the circle is 5 and length of the tangent is 5√3, what is the area of the shaded region?
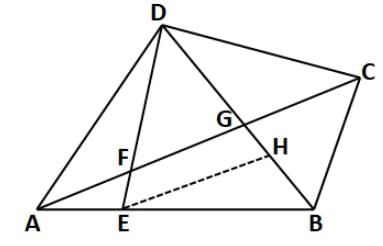
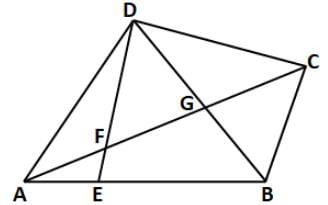
In a quadrilateral ABCD, point E lies on side AB such that AE:EB = 2:3. If the point F, divides DE in 8:3 and DG = 20 cm, then find out the area of △BGC to that of △DGC.
The minimum value of the expression |x+3|+|x-3|+|x-6|+|x-5|+|x+5|
Find the number of non-negative integral points that satisfy 2x + y > 16 and x + 2y = 20.
Which condition will a,b,c satisfy if the set of equations 3x + 4y + z = a, 2x + 6y + 4z = b and x - y - 2z = c has atleast 1 solution ? Also a + b + c ≠ 0.
Solve for x in the following equation:
log 10 (x−1) + log10 (2x-1)= 2 * log10 (x+1)
If (|log (6x+4) (3x−2)|)=1. What is the number of possible values of x?
Find the product of all the values of 3x+2 such that the values of x satisfy the following equation: log3(18 - 3x) =3−x.
What is the sum of all multiples of 3 less than 1000 which give an odd remainder when divided by 11 ?
A dishonest shopkeeper sells sugar at cost price but makes 25% profit by using faulty weights. He decides to give a discount to attract more customers. What percent of discount should he offer to make 12% profit?
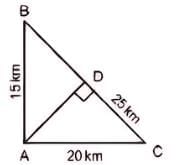
Let ABC be a right-angled triangle with BC as the hypotenuse. Lengths of AB and AC are 15 km and 20 krn, respectively. The minimum possible time, in minutes, required to reach the hypotenuse from A at a speed of 30 km per hour is
If a, b, c, and d are integers such that a + b + c + d = 30, then the minimum possible value of
(a - b)2 + (a - c)2 + (a - d)2 is
DIRECTIONS for the question: Solve the following question and mark the best possible option.
A person can complete a job in 120 days. He works alone on Day 1. On Day 2, he is joined by another person who also can complete the job in exactly 120 days. On Day 3, they are joined by another person of equal efficiency. Like this, everyday a new person with the same efficiency joins the work. How many days are required to complete the job?


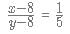
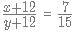

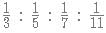
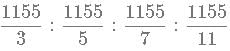 which is equivalent to
which is equivalent to 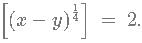 The square bracket represent integer function.
The square bracket represent integer function.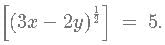
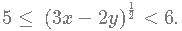
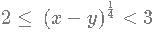
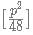 when p is even and
when p is even and 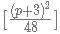 when p is odd, where [] is the nearest integer function.
when p is odd, where [] is the nearest integer function.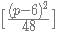 when p is even and
when p is even and 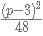 if p is odd.
if p is odd.