Accountancy: CUET Mock Test - 1 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET Mock Test Series - Accountancy: CUET Mock Test - 1
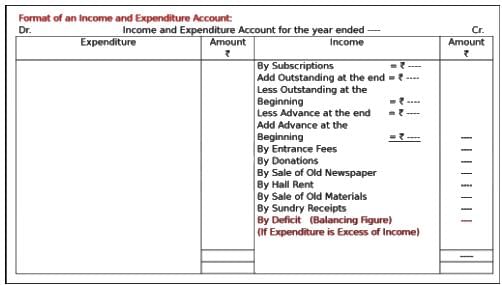
Specific donations are ________ for non profit organisation.
Which of the following is a major income for non-profit organisation?
The profit amount received for sale of old sports materials by a Non-profit organisation is shown in which of the following?
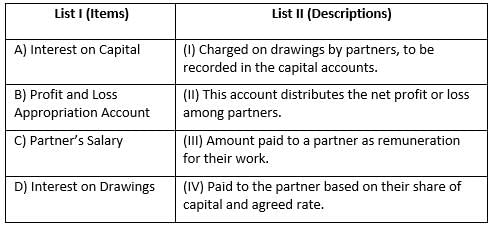
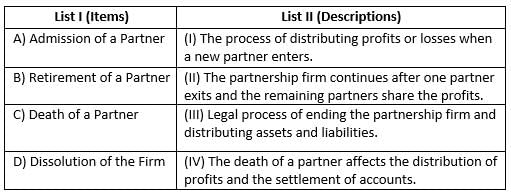
Loan of Partners amount paid out of the amount realized in case of Dissolution of a Partnership firm:
While calculating Goodwill under super profit method, the sequence followed is :
(A) Calculation of Super profit
(B) Calculation of Capital Employed
(C) Calculation of Normal profit
(D) Calculation of Average profit
(E) Calculation of Goodwill
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Identify the correct sequence to be followed at the time of Retirement of a Partner:
(A) New Balance Sheet after Retirement
(B) Transferring balance to Retiring partner's Loan Account
(C) Calculation Gaining/Sacrificing Ratio
(D) Partners' Capital Account
(E) Preparation of Revaluation Account
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
If the profit for the year ended 31st March 2018 was Rs. 2,40,000, how much would be C's share of the profit for that year?
What is the basis for calculating the deceased partner C’s share in the partnership's profits?
What is the significance of March 31st in the context of the partnership?
According to the partnership deed, the calculation of a deceased partner's share in profit is based on:
Which of the following statements are true?
A) Common-size balance sheet shows the relative value of the various items.
B) In the common size income statement, each product is represented as a percentage of the net sales figure.
C) Common size income statements represent the various elements as a percentage of the gross profit
Which of the following statements are false?
(i) Comparative Financial Statement is an indicator of trend and helps in forecasting.
(ii) In Common Size Financial Statement, 100% is taken as base and all other related amounts are expressed as a percentage of base.
(iii) Analysis through Comparative Financial Statement is also known as Horizontal Analysis.
Choose from the following Options:
What does the term "debentures" refer to in this passage?
Why do companies prefer debentures for raising long-term funds?
What is another term used for the funds raised through debentures?
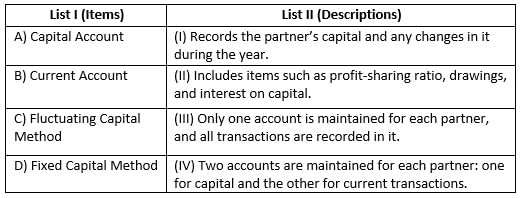
In absence of partnership deed, ______ partner gets more share of profit.
|
39 docs|148 tests
|