Economics: CUET Mock Test - 3 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET Mock Test Series - Economics: CUET Mock Test - 3
Choose the correct chronological order:
A. India's first official census
B. Opening of the Suez Canal
C. Introduction of Railways in India
D. Green Revolution
E. Set up of the Planning Commission
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Categorize the following as induced investment and autonomous investment.
Government has set up public health centres in rural areas.
Human Development Index (HDI) is entrusted with reference to:
1. Life expectancy at birth
2. GNP per capita
3. Infant mortality
4. Morbidity
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Current Account components of trade in services include:
(A) Gifts, Remittances
(B) Net Non-Factor Income
(C) Net Investment Income
(D) Grants
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
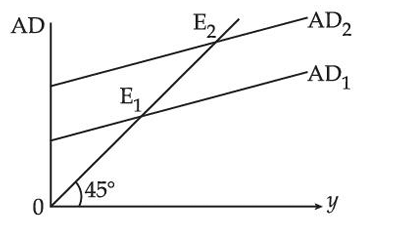
The aggregate demand line shifts parallel upwards. The reason behind this is :
The gold standard system of exchange rate lost its importance during
Which of the following countries still follows fixed exchange rate system?
The ________ expresses the ratio of exchange between the currencies of two countries.
Devaluation of currency is a component of _______ exchange rate system.
What will be the most likely impact on the national income when in a country the price of foreign currency rises, keeping other things unchanged?
Before the Bretton Woods standard system, exchange rates were pegged against ______
Suppose the government plans to reduce the prices of US Dollar from ₹ 50 to ₹ 45. This step is known as ............ of domestic currency.
The fixed exchange rate is determined by the Reserve Bank of India.
Increase in the value of domestic commodities in terms of foreign currency is known as
Relationship between demand for foreign exchange and foreign exchange rate is
A downward movement along the demand curve for foreign exchange indicates
he US $ exchange rate for rupee is ₹ 75 now, as compared to ₹ 63 previously. This shows that the value of rupee has
Currency appreciation depicts a situation when domestic currency gains its value in relation to a foreign currency.
Under managed floating exchange rate system, central bank determines the exchange rate and excessive fluctuation is checked by the market forces.
If ₹ 75 are required to buy 1$, instead of ₹ 78 per US Dollar, this situation is indicating that
Clean floating exchange rate is determined at a point where
It has been observed in recent times that Indian currency is depreciating against US Dollar. Which of the following reason can be accounted for the same?
Assertion (A): Demand for foreign exchange and exchange rate moves in the same direction.
Reason (R): When exchange rate rises domestic goods becomes cheaper in international market.
Alternatives
Assertion (A): Manage floating exchange rate system is a hybrid system of exchange rate used by the most of the countries in recent time.
Reason (R): Excessive fluctuation in exchange rate system is checked by the central authority under dirty floating exchange rate.
Alternatives
|
8 docs|148 tests
|




















