Economics: CUET Mock Test - 4 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET Mock Test Series - Economics: CUET Mock Test - 4
Reserves arising from capital receipts are known as:
Consider the following statements.
1. Capital receipts are the amount received in the form of taking loans and selling of any fixed asset.
2. Capital receipts either decrease the liability or increase the asset.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
The market for sugar is in equilibrium. If the supply of sugar increases, the equilibrium price of sugar will ________ and the equilibrium quantity will _________.
Arrange the following in chronological order of their occurrence in India.
(A) The second stage of demographic transition began
(B) Incorporation of Tata Iron and Steel company
(C) British India first census
(D) Introduction of railways
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The Industrial policy closely related to the trade Policy which aimed at replacing imports with domestic production is known as:
Match List - I with List - II.
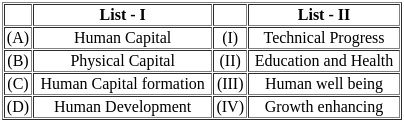
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Generally, the value of currency of a country is expressed in terms of ________
Increase in the value of foreign commodities in term of domestic currency as planned by the government refers to
The curve depicting the supply of foreign exchange i s ________ sloped.
Demand for foreign exchange is directly related to the price of foreign exchange.
Devaluation and depreciation of currency are one or the same thing.
The market where foreign currencies are traded is known as
Indian government initiated many schemes to attract foreign investment, which of the following statement is correct from below
Due to appreciation of domestic currency, supply curve of foreign exchange will
Flexible exchange rate is determined by the supply and demand of foreign exchange in the international market.
Appreciation of foreign currency leads to increase in exports from the domestic country.
Occasional intervention by central bank to influence price of foreign exchange is known as .............
The form of exchange market in which delivery of currency happens on the same day is known as
Assertion (A): Make in India campaign initiated by the government leads to rise in foreign exchange rate.
Resason (R): Inflow of foreign exchange improves the trade deficit of the country.
Alternatives
Assertion (A): Manage floating exchange rate system is a hybrid system of exchange rate used by the most of the countries in recent time.
Reason (R): Excessive fluctuation in exchange rate system is checked by the central authority under dirty floating exchange rate.
Alternatives
Directions: Read the following case study and answer the questions.
Indian’s exchange rate policy has evolved in line with international and domestic developments. Post-independence, in view of the prevailing Bretton Woods system, the Indian rupee was pegged to the Pound sterling. With the breakdown of the Bretton Woods system, and also the declining share of UK in India’s trade, the rupee was delinked from the Pound sterling in September, 1975. During the period between 1975 to 1992, the exchange rate was officially determined by the RBI within nominal band of plus or minus 5 percent of the weighted basket of currencies of India’s major trading partners. This exchange rate was referred to as ‘adjustable nominal peg with a band’.
Q. Post-independence, the exchange rate was determined under
Directions: Read the following case study and answer the questions.
Indian’s exchange rate policy has evolved in line with international and domestic developments. Post-independence, in view of the prevailing Bretton Woods system, the Indian rupee was pegged to the Pound sterling. With the breakdown of the Bretton Woods system, and also the declining share of UK in India’s trade, the rupee was delinked from the Pound sterling in September, 1975. During the period between 1975 to 1992, the exchange rate was officially determined by the RBI within nominal band of plus or minus 5 percent of the weighted basket of currencies of India’s major trading partners. This exchange rate was referred to as ‘adjustable nominal peg with a band’.
Q. Immediately after independence, Indian rupee was pegged to the ______
Directions: Read the following case study and answer the questions.
Indian’s exchange rate policy has evolved in line with international and domestic developments. Post-independence, in view of the prevailing Bretton Woods system, the Indian rupee was pegged to the Pound sterling. With the breakdown of the Bretton Woods system, and also the declining share of UK in India’s trade, the rupee was delinked from the Pound sterling in September, 1975. During the period between 1975 to 1992, the exchange rate was officially determined by the RBI within nominal band of plus or minus 5 percent of the weighted basket of currencies of India’s major trading partners. This exchange rate was referred to as ‘adjustable nominal peg with a band’.
Q. The rupee was delinked from Pound sterling in 1975 because
Directions: Read the following case study and answer the questions.
Indian’s exchange rate policy has evolved in line with international and domestic developments. Post-independence, in view of the prevailing Bretton Woods system, the Indian rupee was pegged to the Pound sterling. With the breakdown of the Bretton Woods system, and also the declining share of UK in India’s trade, the rupee was delinked from the Pound sterling in September, 1975. During the period between 1975 to 1992, the exchange rate was officially determined by the RBI within nominal band of plus or minus 5 percent of the weighted basket of currencies of India’s major trading partners. This exchange rate was referred to as ‘adjustable nominal peg with a band’.
Q. Indian currency was delinked from pound sterling on
|
8 docs|148 tests
|




















