Economics: CUET Mock Test - 8 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET Mock Test Series - Economics: CUET Mock Test - 8
Ford Motors entered the Indian automobile business in collaboration with which Indian manufacturer?
Development expenditure does not include expenditure on
Match List - I with List - II.
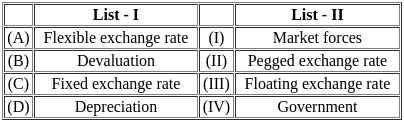
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Which of the following will be included in the National Income of India ?
(A) Donations given to a religious institution.
(B) Payment of Income Tax
(C) Scholarship given to students
(D) Profits earned by an Indian company from its branch in France
(E) Purchase of a television set by a consumer household
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Arrange the sequence of events relating to identifying the number of poor in India.
(A) Task force on projection of minimum needs and effective demand formed
(B) Expert groups formed
(C) Planning Commission formed a study group
(D) Dadabhai Naoroji formulated the 'Jail cost of living'
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Revenue Receipts in the government budget include :
(A) Government Borrowings
(B) Tax Revenue
(C) Interest receipts on loans by government
(D) Dividends earned by government on its investment
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
One major factor that has stimulated the globalisation process is:
Which out of the following is an example of a trade barrier?
Cargill Foods, an MNC has bought over which indigenous Indian company?
What is happening with the import of Chinese toys in India ?
If tax is imposed on Chinese toys, what will happen?
Removing barriers or restrictions set by the government is called:
Which out of the following industries has a large number of well-off buyers in urban areas?
One major government initiative to attract foreign companies to invest in India is:
With the growing competition, most employers these days prefer to employ workers:
Disinvestment means selling of a public investment to a ______:
|
39 docs|147 tests
|




















