Geography: CUET Mock Test - 6 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET Mock Test Series - Geography: CUET Mock Test - 6
Which among the following statements is correct in context of human geography?
Paper industry is mainly associated with which of the following industries?
The first complete population census in India was conducted in which of the following years?
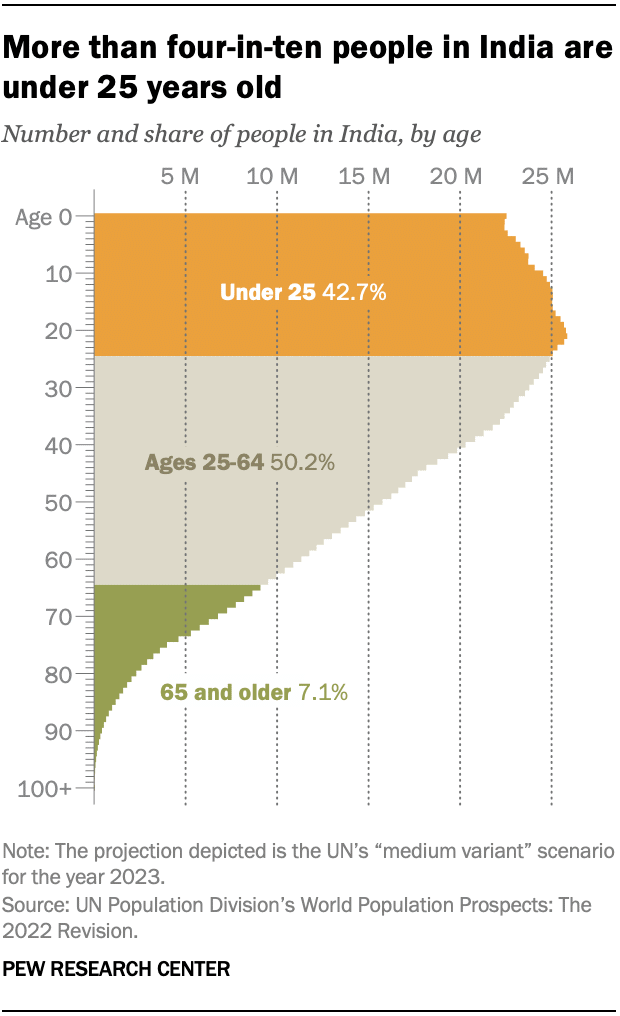
Which among the following factors influence the density distribution of the population in India?
1. Amount of rainfall
2. Cultural factors
3. Distribution of minerals
4. Fertility of soils
Select the correct answer from the options given below.Consider the following pairs regarding the different Age-Groups:
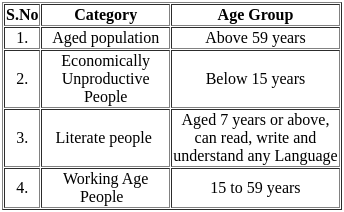
How many pairs is/are correctly matched?
What is one of the strategies mentioned in the passage to cope with the impacts of climate change?
The passage mentions the importance of climate models in understanding the interactions between various elements. Which of the following is NOT listed as one of these elements?
What global effort is mentioned in the passage as aiming to mitigate climate change?
What tool is especially important in understanding and predicting climate change?
What is the primary driver of international cooperation and foreign policies, as mentioned in the passage?
What risk do oil-exporting economies specifically face during the transition away from fossil fuels?
According to the passage, what should be a priority for countries in the context of the energy transition?
What consequences are associated with the increased extraction of fossil fuels and minerals, as stated in the passage?
What role does climate diplomacy play in addressing the challenges of the energy transition?
Which of the following sea routes connects Western Europe to Australia via the Panama Canal?
Name the gauge in which distance between the rails is 0.762 metre or 0.610 metre.
Where in Brazil did more than 100 heads of states meet for the inaugural International Earth Summit in June 1992?
Where and when did the first railway line for the general public open?
Which of the following statements is/are true in context of ferrous mineral and their presence in India?
Which of the following statements regarding alluvial soils is/are true?
Statement I: The Himalayan river systems deposit alluvial soils in the south of India, giving rise to the entire southern plains.
Statement II: On the basis of age, alluvial soil can be categorised into three kinds.
In which year was the Indian National Satellite System (INSAT) established?
Which of the following is not the pattern of rural settlement?
Which of the following statements about Agenda 21 is/are true?
_____________ was introduced by the government of India in 2015 to address the issue of decline in child sex ratio.
|
39 docs|148 tests
|