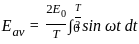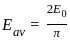Physics: CUET Mock Test - 8 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Physics: CUET Mock Test - 8
A capacitor of capacitance 5μF is charged to a potential difference of 20V. After that, it is connected across an inductor of inductance 0.5 mH. What is the current flowing in the circuit at a time when the potential difference across the capacitor is 10 V?
A circuit element 'X' when connected to peak voltage of 200 V, a peak current of 5A flows which lags behind the voltage by π/2. A circuit element Y when connected to same peak voltage, same peak current flows which is in phase with the voltage. Now X and Y are connected in series with same peak voltage. The rms value of current through the circuit will be:
To increase magnification power of refracting type Telescope, we should increase :
X-rays are different from UV light because it has different __________ from UV light.
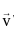 = (3î + 4ĵ) m/s in a uniform magnetic field of B = 5 k̂T. What is the magnetic force experienced by the charge?
= (3î + 4ĵ) m/s in a uniform magnetic field of B = 5 k̂T. What is the magnetic force experienced by the charge?
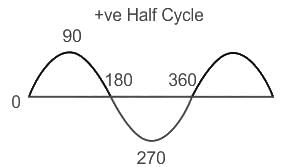
The average e.m.f. during the positive half cycle of an A.C. supply of peak value E0 is:
The intensity of a plane electromagnetic wave is proportional to
The direction of propagation of an electromagnetic plane wave is
Which of the following is true about equipotential lines?
In electrolytic capacitors positive terminal is ________
If a positive charge moves opposite to the direction of the electric field :
The maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted from a surface when photons of energy 6 eV fall on it is 4 eV. The stopping potential is
If maximum velocity with which an electron can be emitted from a photo cell is 3.75×108cms−1 then stopping potential is
Suppose you are given a chance to repeat the alpha-particle scattering experiment using a thin sheet of solid hydrogen in place of the gold foil. (Hydrogen is a solid at temperatures below 14 K.) What results do you expect?
A sample of radioactive material contains 1018 atoms. The half life of the material is 2 days, then the activity of the sample is
What is the most common application of LC oscillators?
Which one of the following, when suspended freely, slowly sets itself parallel to the direction of the magnetic field?
Identify the direction in which a thin long piece of magnet comes to rest when suspended freely.
A magnetic dipole of length 10 cm has pole strength of 20 Am. Find the magnetic moment of the dipole.


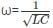
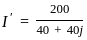
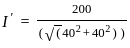


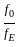
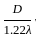
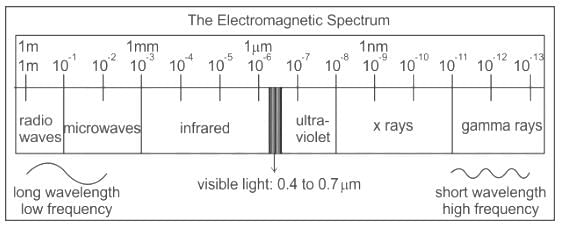
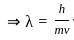
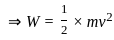 -----(2)
-----(2)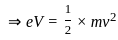
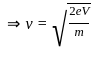 -----(3)
-----(3)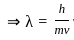 -----(4)
-----(4)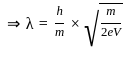
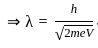
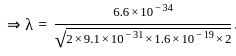
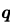
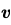
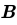
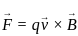
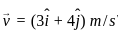 , Uniform magnetic Field,
, Uniform magnetic Field, 
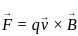
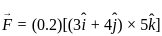
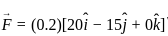
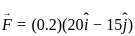
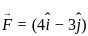
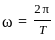 ---- (3)
---- (3)