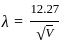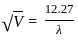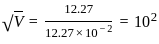Physics: CUET Mock Test - 9 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Physics: CUET Mock Test - 9
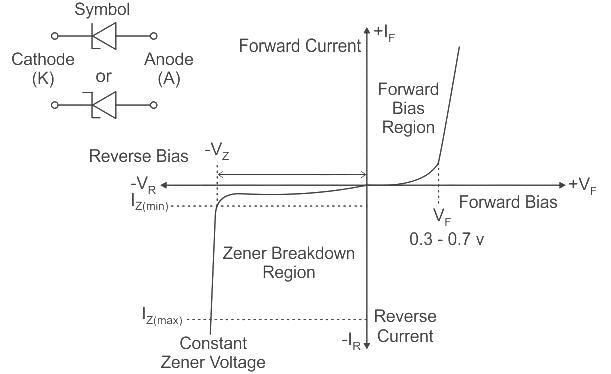
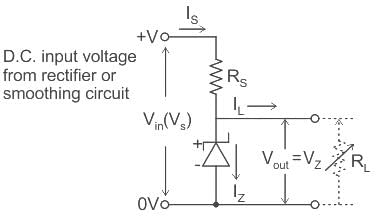
Which of the following is a widely used variety of commercial resistor?
The radius of the innermost electron orbit of a hydrogen atom is 5.3 × 10–11 m. The radius of the n = 3 orbit is
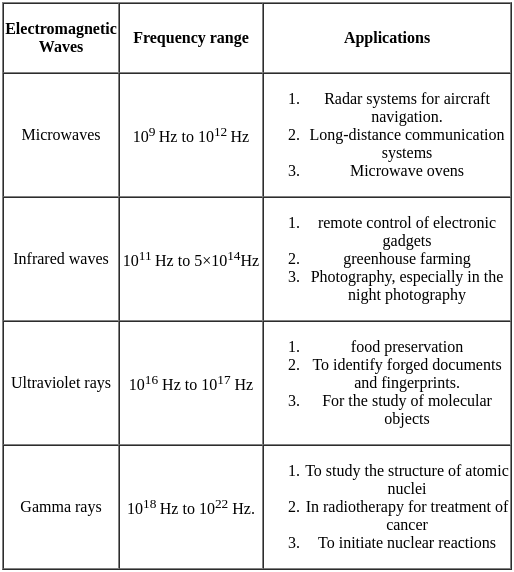
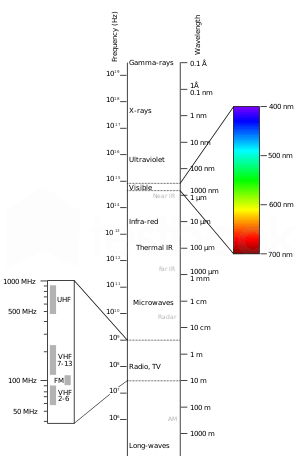
The decreasing order of wavelength of infrared, microwave, ultraviolet and gamma rays is
What is the order of potential difference built up by the Van de Graff generator?
What is the primary function of a Van de Graaff generator in electrostatic experiments?
If the length of the filament of a heater is reduced by 10% the power of the heater will
The instrument for the accurate measurement of the e.m.f of a cell is
A piece of copper and another of germanium are cooled from room temperature to 80K. The resistance
A Wheatstone bridge is balanced for four resistors R1, R2, R3 and R4 with a Lech lanche cell between A and C and a galvanometer between B and D. The positions of the cell and the galvanometer are interchanged. The balance will
The electric current in a discharge tube containing a gas is due to
A steady current is passing through a linear conductor of non-uniform cross-section. The current density in the conductor is
Two wires each of radius of cross section r but of different materials are connected together end to end (in series). If the densities of charge carriers in the two wires are in the ratio 1 : 4, the drift velocity of electrons in the two wires will be in the ratio.
Read the following statements carefully:
Y: The resistivity of a semiconductor decreases with increases of temperature.
Z: In a conducting solid, the rate of collision between free electrons and ions increases with increase of temperature.
Select the correct statement from the following
A storage battery is connected to a charger for charging with a voltage of 12.5 Volts. The internal resistance of the storage battery is 1 ohm. When the charging current is 0.5 A, the emf of the storage battery is :
A galvanometer of resistance 70Ω, is converted to an ammeter by a shunt resistance rs = 0.03Ω. The value of its resistance will become
The conversion of a moving coil galvanometer into a voltmeter is done by
The magnetic moment associated with a circular coil of 35 turns and radius 25cm, if it carries a current of 11A is
A short bar magnet has a magnetic moment of 0.65JT−1, then the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field produced by the magnet at a distance 8cm from the centre of magnet on the axis is
A circular coil of radius 10cm having 100 turns carries a current of 3.2A. For the coil given the magentic moment is
A current carrying loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field. The torque acting on it does not depend upon



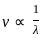 -------(1)
-------(1)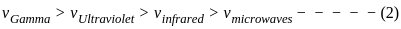

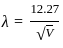
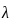 is the wavelength in °A and V in Volt is the potential difference.
is the wavelength in °A and V in Volt is the potential difference.