Psychology: CUET Mock Test - 2 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CUET Mock Test Series - Psychology: CUET Mock Test - 2
Karim watches TV when he is stressed due to pending assignments in school. According to Endler and Parker, he is using _________ mechanism of coping.
Increase in the value of one variable with the decrease in the value of the other variable implies
Behavioural Analysis to assess personality contains data obtained from which of the following tests?
1. Interview
2. Nomination
3. Observation
4. Ratings
Choose the correct answer using the codes given below:
_______ results from the blocking of needs and motives by something or someone that hinders us from achieving a desired goal.
__________ is the term used to describe the level of stress that is good for you.
The ______ Model explains the influence of stress on the body.
Creative visualisation is a subjective experience that uses __________ and imagination.
Family and friends also provide__________ support about stressful events.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): An individual’s response to a stressful situation largely depends upon the perceived events and how they are interpreted or appraised.
Reason (R): Lazarus has distinguished between two types of appraisals, i.e., primary and secondary.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): To manage stress, we often need to reassess the way we think and learn coping strategies.
Reason (R): People who cope poorly with stress have an impaired immune response and diminished activity of natural killer cells.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): After visualising one must set oneself a realistic goal, as it helps build confidence.
Reason (R): It is easier to visualise if one’s mind is quiet, body is relaxed and eyes are closed.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion (A): Psychological stresses are caused when we overexert ourselves physically, lack a nutritional diet, suffer an injury or fail to get enough sleep.
Reason (R): Environmental stresses are caused by air pollution, crowding, noise, heat of the summer, winter cold or disasters such as fire, or natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, drought, land-slides, volcanic eruptions, etc.
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct option:
Stress factors broadly fall into three types or categories: physical stress, psychological stress and psychosocial stress.
Physical stress: trauma (injury, infection, surgery), intense physical labour/over-exertion, environmental pollution (pesticides, herbicides, toxins, heavy metals, inadequate light, radiation, noise, electromagnetic fields), illness (viral, bacterial, or fungal agents), fatigue, inadequate oxygen supply, hypoglycaemia I (low blood sugar), hormonal and/or biochemical imbalances, dietary stress (nutritional deficiencies, food allergies and sensitivities, unhealthy eating habits), dehydration, substance abuse, dental challenges, and musculoskeletal misalignments/imbalances.
Psychological stress: emotional stress (resentments, fears, frustration, sadness, anger, grief/bereavement), cognitive stress (information overload, accelerated sense of time, worry, guilt, shame, jealousy, resistance, attachments, selfcriticism, self-loathing, unworkable perfectionism, anxiety, panic attacks, not feeling like yourself, not feeling like things are real, and a sense of being out of control/not being in control), and perceptual stress (beliefs, roles, stories, attitudes, world view).
Psychosocial stress: relationship/marriage difficulties (partner, siblings, children, family, employer, co-workers, employer), lack of social support, lack of resources for adequate survival, loss of employment/investments/savings, loss of loved ones, bankruptcy, home foreclosure, and isolation. Overall, improperly or ineffectively managed stress usually takes a toll on the body. When stress related feelings, moods, emotions are pushed into the body, the soma, this is usually termed psychosomatic or psychogenic illness, including headaches, heart palpitations, physical/ cognitive/emotional pain and suffering, constricted
throat and shallow, constricted breathing, clammy palms, fatigue, nausea, anxiety, allergies, asthma, autoimmune syndromes related to an ineffective functioning of the immune system, hypertension (high blood pressure), and gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhoea, upset stomach, duodenal ulcers and oesophageal reflux syndrome.
Q. Which of the following doesn’t fall under the broad category of stress?
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct option:
Stress factors broadly fall into three types or categories: physical stress, psychological stress and psychosocial stress.
Physical stress: trauma (injury, infection, surgery), intense physical labour/over-exertion, environmental pollution (pesticides, herbicides, toxins, heavy metals, inadequate light, radiation, noise, electromagnetic fields), illness (viral, bacterial, or fungal agents), fatigue, inadequate oxygen supply, hypoglycaemia I (low blood sugar), hormonal and/or biochemical imbalances, dietary stress (nutritional deficiencies, food allergies and sensitivities, unhealthy eating habits), dehydration, substance abuse, dental challenges, and musculoskeletal misalignments/imbalances.
Psychological stress: emotional stress (resentments, fears, frustration, sadness, anger, grief/bereavement), cognitive stress (information overload, accelerated sense of time, worry, guilt, shame, jealousy, resistance, attachments, selfcriticism, self-loathing, unworkable perfectionism, anxiety, panic attacks, not feeling like yourself, not feeling like things are real, and a sense of being out of control/not being in control), and perceptual stress (beliefs, roles, stories, attitudes, world view).
Psychosocial stress: relationship/marriage difficulties (partner, siblings, children, family, employer, co-workers, employer), lack of social support, lack of resources for adequate survival, loss of employment/investments/savings, loss of loved ones, bankruptcy, home foreclosure, and isolation. Overall, improperly or ineffectively managed stress usually takes a toll on the body. When stress related feelings, moods, emotions are pushed into the body, the soma, this is usually termed psychosomatic or psychogenic illness, including headaches, heart palpitations, physical/ cognitive/emotional pain and suffering, constricted
throat and shallow, constricted breathing, clammy palms, fatigue, nausea, anxiety, allergies, asthma, autoimmune syndromes related to an ineffective functioning of the immune system, hypertension (high blood pressure), and gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhoea, upset stomach, duodenal ulcers and oesophageal reflux syndrome.
Q. When stress-related feelings, moods, emotions are pushed into the body, it is called
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct option:
Hans Selye, a Vienna-born scientist, working in the 20th century, was the first person to describe GAS. Selye found that rats displayed a similar set of physical responses to several different stressors. The latter included cold temperatures, excessive physical exertions, and injection with toxins. The scientist explained GAS as the body’s way of adapting to a perceived threat to better equip it to survive. A paper on Selye’s GAS theory was published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology in 1946. The three stages of GAS are:
(A) Alarm reaction
(B) Resistance
(C) Exhaustion
When does GAS occur? Selye’s study was limited to physical stressors, such as cold temperatures and physical overexertion. However, it is now understood that life events that induce psychological stress cause the same physical reactions, as were seen in Selye’s study. The sort of life events that can cause a person to experience stress and GAS include (relationship breakdowns, losing a job, medical problems and money troubles) In theory, the fact that these situations can cause GAS may be beneficial. The alarm reaction gives people a burst of energy and concentration that could help them to problem-solve. For most people, however, the physical response their body goes through when they are under stress is not helpful. Unlike threats people may have faced in the Stone Age, a person nowadays is unlikely to be able to resolve a stressful situation of modernday life with a burst of energy. Long-term stress can have a negative impact on a person physically and on their immune system. A 2008 paper noted that chronic stress could lead to increase the risk of viral infection, stomach ulcers, depression and heart disease.
Q. Hans Seyle was born in
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct option:
Hans Selye, a Vienna-born scientist, working in the 20th century, was the first person to describe GAS. Selye found that rats displayed a similar set of physical responses to several different stressors. The latter included cold temperatures, excessive physical exertions, and injection with toxins. The scientist explained GAS as the body’s way of adapting to a perceived threat to better equip it to survive. A paper on Selye’s GAS theory was published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology in 1946. The three stages of GAS are:
(A) Alarm reaction
(B) Resistance
(C) Exhaustion
When does GAS occur? Selye’s study was limited to physical stressors, such as cold temperatures and physical overexertion. However, it is now understood that life events that induce psychological stress cause the same physical reactions, as were seen in Selye’s study. The sort of life events that can cause a person to experience stress and GAS include (relationship breakdowns, losing a job, medical problems and money troubles) In theory, the fact that these situations can cause GAS may be beneficial. The alarm reaction gives people a burst of energy and concentration that could help them to problem-solve. For most people, however, the physical response their body goes through when they are under stress is not helpful. Unlike threats people may have faced in the Stone Age, a person nowadays is unlikely to be able to resolve a stressful situation of modernday life with a burst of energy. Long-term stress can have a negative impact on a person physically and on their immune system. A 2008 paper noted that chronic stress could lead to increase the risk of viral infection, stomach ulcers, depression and heart disease.
Q. The events that can cause an individual to experience GAS are
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct option:
A Measure of Stressful Life Events
Holmes and R ahe developed a life event measure of stress. A measure of stressful life events based on the above scale known as the Presumptive Stressful Life Events Scale has been developed for the Indian population by Singh, Kaur and Kaur. It is a self-rating questionnaire made up of fifty-one life changes, which a person may have experienced. Each of these life events is assigned a numerical value in terms of their severity. For example, the death of one’s spouse is assigned 95, personal illness or injury 56, failure in examination 43, appearing for examination or interview 43, change in sleeping habits 33, as the mean stress score. Both positive and negative events are taken, believing that both kinds of changes cause stress. The respondent’s stress score is the weighted sum of all the items/life change events in the past one year checked by her/him.
Some sample items of the measure are :
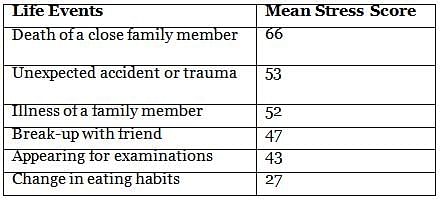
The mean number of stressful life events experienced over a period of one year without producing overt physical or mental illness is approximately two. However, the correlations between life events and susceptibility to any particular illness is low, indicating a weak association between life events and stress. It has been argued as to whether life events have caused some stress-related illness or whether stress caused the life events and illness. The impact of most life events varies from person to person. Factors such as age at which the event was first experienced, frequency of occurrence, duration of the stressful event and social support must be studied in evaluating the relationship between stressful life events and the subsequent illness episode.
Q. Which scale has been developed by Singh, Kaur and Kaur?
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow by choosing the correct option:
A Measure of Stressful Life Events
Holmes and R ahe developed a life event measure of stress. A measure of stressful life events based on the above scale known as the Presumptive Stressful Life Events Scale has been developed for the Indian population by Singh, Kaur and Kaur. It is a self-rating questionnaire made up of fifty-one life changes, which a person may have experienced. Each of these life events is assigned a numerical value in terms of their severity. For example, the death of one’s spouse is assigned 95, personal illness or injury 56, failure in examination 43, appearing for examination or interview 43, change in sleeping habits 33, as the mean stress score. Both positive and negative events are taken, believing that both kinds of changes cause stress. The respondent’s stress score is the weighted sum of all the items/life change events in the past one year checked by her/him.
Some sample items of the measure are :

The mean number of stressful life events experienced over a period of one year without producing overt physical or mental illness is approximately two. However, the correlations between life events and susceptibility to any particular illness is low, indicating a weak association between life events and stress. It has been argued as to whether life events have caused some stress-related illness or whether stress caused the life events and illness. The impact of most life events varies from person to person. Factors such as age at which the event was first experienced, frequency of occurrence, duration of the stressful event and social support must be studied in evaluating the relationship between stressful life events and the subsequent illness episode.
Q. How many life changes are self-rated under this scale?
Who defined stress as “the nonspecific response of the body to any demand”?
Frustration is one of the sources of ________ stress.
|
8 docs|148 tests
|