Physics: CUET Mock Test - 2 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Physics: CUET Mock Test - 2
The expression for torque 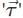 experienced by an electric dipole of dipole moment
experienced by an electric dipole of dipole moment 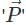 in an external uniform electric field
in an external uniform electric field 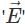 is given by :
is given by :
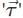 experienced by an electric dipole of dipole moment
experienced by an electric dipole of dipole moment 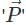 in an external uniform electric field
in an external uniform electric field 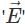 is given by :
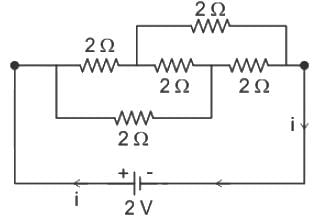
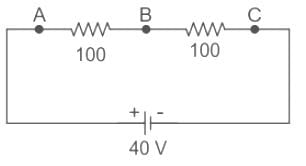
is given by :A voltmeter of resistance 150 Ω is connected across A and B in the given circuit. The reading of voltmeter will be :
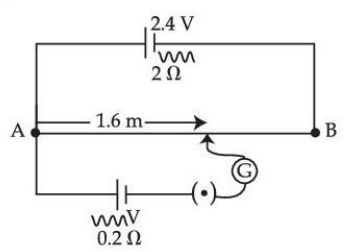
A potentiometer with a cell of 2.4 volt and internal resistance of 2 Ω maintains a potential drop across the resistance wire AB of length 2 meters and resistance 10 Ω. A standard cell which maintains a constant emf of 'V' volt with internal resistance 0.2 Ω gives a balance point at 1.6 m length of the wire. The value of emf of second (standard) cell (V) is:
What torque acts on a 50 turn coil of 200 cm2 area carrying a current of 20 A held with its axis at right angles to a uniform magnetic field of 0.2T?
electromagnetic induction i.e currents can be induced in coils (Select the best)
In an RLC circuit, which of the following is always used as a vector reference?
The speed of electromagnetic waves in free space is given by .
Here μ0 is ___________and ε0 is ________________ of free space.
Which region in the electromagnetic spectrum will have the highest speed?
A ray of light going from denser to rarer medium suffers refraction at a concave surface. Which of the following relations is correct?
Consider a curved surface between two different media with refractive indices n1 = 1 and n2 = 2. The relation between radius of curvature, image distance and object distance is given by
The work function of a photoelectric material is 3.32 eV. The threshold frequency will be equal to
The average angle of deflection of α-particles by a thin gold foil as predicted by Thomson’s model is
The current that exists in the circuit of a photodiode even when no visible light is made incident on it is called
The average lifetime of the first excited level of a hydrogen atom is 1.0 ×10−8 s. In the Bohr model, how many orbits does an electron in the n = 2 level complete before returning to the ground level?
Uniform electric and magnetic fields are produced pointing in the same direction. An electron is projected pointing in the same direction, then