Chemistry: CUET Mock Test - 9 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Chemistry: CUET Mock Test - 9
Which of the following is not a method to test the type of emulsion?
Structure of ammonium salt when ethylamine reacts with one mole of HCl ?
Among the following amines, which one is most basic (in aqueous solution)?
The correct order of basicity of amines in gas phase
Among the following, which one has the highest pKb value?
Among the following, which one has the highest Kb value?
What is the colligative property that is being discussed in the passage?
What is the relationship between the change in boiling point (ΔT_b) and the concentration of solute particles?
In the equation ΔT_b = K_b × m, what does 'm' represent?
What is the effect of adding a non-volatile solute like NaCl on the boiling point of water?
Why is the solution of NaCl considered a non-volatile solute?
Which of the following alcohols is dehydrated most readily with conc. H2SO4.
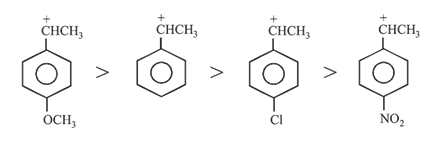
Which one of the following compounds has the most acidic nature?
The strongest acid among the following aromatic compounds is
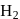 in presence of
in presence of 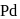 and
and 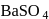 gives:
gives:
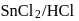 is used in which of the following method of synthesis of aldehyde?
is used in which of the following method of synthesis of aldehyde?
The incorrect statement regarding oxo process for synthesis of an aldehyde is


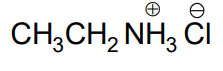

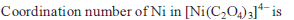

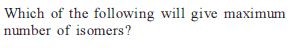
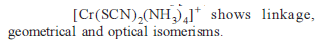
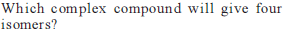
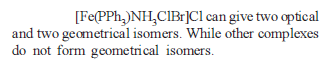



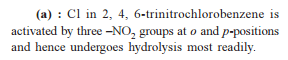
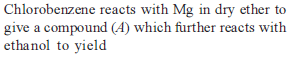
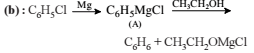

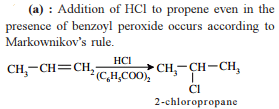
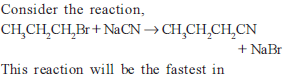
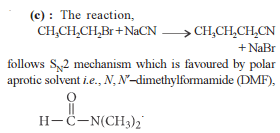
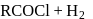
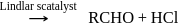
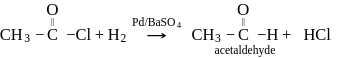
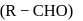 from nitriles
from nitriles 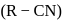 using
using 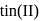 chloride
chloride 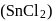 , hydrochloric acid
, hydrochloric acid  and quenching the resulting iminium salt ([R
and quenching the resulting iminium salt ([R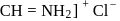 ) with water
) with water 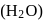 .
.