Test: Cold War Era and Non–aligned Movement- Case Based Type Questions (Old Syllabus) - Humanities/Arts MCQ
16 Questions MCQ Test Political Science Class 12 - Test: Cold War Era and Non–aligned Movement- Case Based Type Questions (Old Syllabus)
Which of the following countries is a member of both NATO and CENTO?
Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows:
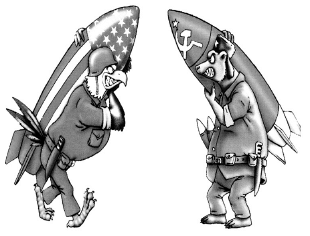
Q. What was the result of the Cold War?

Which one of the following reforms was not promised by Gorbachev?
Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows:
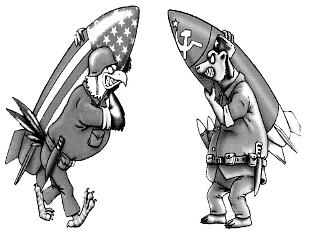
Q. Name two allied countries each of these superpowers.
'Bay of Pigs' refers to
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
In April 1961, the leaders of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) were worried that the United States of America (USA) would invade communist-ruled Cuba and overthrow Fidel Castro, the president of the small island nation off the coast of the United States. Cuba was an ally of the Soviet Union and received both diplomatic and financial aid from it. Nikita Khrushchev, the leader of the Soviet Union, decided to convert Cuba into a Russian base. In 1962, he placed nuclear missiles in Cuba. The installation of these weapons put the US, for the first time, under fire from close range and nearly doubled the number of bases or cities in the American mainland which could be threatened by the USSR. Three weeks after the Soviet Union had placed the nuclear weapons in Cuba, the Americans became aware of it. The US President, John F. Kennedy, and his advisers were reluctant to do anything that might lead to full-scale nuclear war between the two countries, but they were determined to get Khrushchev to remove the missiles and nuclear weapons from Cuba. Kennedy ordered American warships to intercept any Soviet ships heading to Cuba as a way of warning the USSR of his seriousness. A clash seemed imminent in what came to be known as the Cuban Missile Crisis. The prospects of this clash made the whole world nervous, for it would have been no ordinary war. Eventually, to the world’s great relief, both sides decided to avoid war. The Soviet ships slowed down and turned back.
Q. Who ordered American warships to intercept any Soviet ships heading to Cuba as a way of warning to USSR?
The unification of Germany was completed as a result of
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
In April 1961, the leaders of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) were worried that the United States of America (USA) would invade communist-ruled Cuba and overthrow Fidel Castro, the president of the small island nation off the coast of the United States. Cuba was an ally of the Soviet Union and received both diplomatic and financial aid from it. Nikita Khrushchev, the leader of the Soviet Union, decided to convert Cuba into a Russian base. In 1962, he placed nuclear missiles in Cuba. The installation of these weapons put the US, for the first time, under fire from close range and nearly doubled the number of bases or cities in the American mainland which could be threatened by the USSR. Three weeks after the Soviet Union had placed the nuclear weapons in Cuba, the Americans became aware of it. The US President, John F. Kennedy, and his advisers were reluctant to do anything that might lead to full-scale nuclear war between the two countries, but they were determined to get Khrushchev to remove the missiles and nuclear weapons from Cuba. Kennedy ordered American warships to intercept any Soviet ships heading to Cuba as a way of warning the USSR of his seriousness. A clash seemed imminent in what came to be known as the Cuban Missile Crisis. The prospects of this clash made the whole world nervous, for it would have been no ordinary war. Eventually, to the world’s great relief, both sides decided to avoid war. The Soviet ships slowed down and turned back.
Q. Who decided to convert Cuba into a Russian base?
When did Czechoslovakia dissolve to form the Czech Republic and Slovakia?
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
The end of the Second World War is a landmark in contemporary world politics. In 1945, the Allied Forces, led by the US, Soviet Union, Britain and France defeated the Axis Powers led by Germany, Italy and Japan, ending the Second World War (1939- 1945). The war had involved almost all the major powers of the world and spread out to regions outside Europe including Southeast Asia, China, Burma (now Myanmar) and parts of India’s northeast. The war devastated the world in terms of loss of human lives and civilian property. The First World War had earlier shaken the world between 1914 and 1918.The end of the Second World War was also the beginning of the Cold War. The world war ended when the United States dropped two atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945, causing Japan to surrender. Critics of the US decision to drop the bombs have argued that the US knew that Japan was about to surrender and that it was unnecessary to drop the bombs. They suggest that the US action was intended to stop the Soviet Union from making military and political gains in Asia and elsewhere and to show Moscow that the United States was supreme. US supporters have argued that the dropping of the atomic bombs was necessary to end the war quickly and to stop further loss of American and Allied lives. Whatever the motives, the consequence of the end of the Second World War was the rise of two new powers on the global stage. With the defeat of Germany and Japan, the devastation of Europe and in many other parts of the world, the United States and the Soviet Union became the greatest powers in the world with the ability to influence events anywhere on earth.
Q. What is the critics’ opinion about USA dropping the atomic bombs on Japan?
Who was the chief architect of the unification of Germany?
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
The end of the Second World War is a landmark in contemporary world politics. In 1945, the Allied Forces, led by the US, Soviet Union, Britain and France defeated the Axis Powers led by Germany, Italy and Japan, ending the Second World War (1939- 1945). The war had involved almost all the major powers of the world and spread out to regions outside Europe including Southeast Asia, China, Burma (now Myanmar) and parts of India’s northeast. The war devastated the world in terms of loss of human lives and civilian property. The First World War had earlier shaken the world between 1914 and 1918.The end of the Second World War was also the beginning of the Cold War. The world war ended when the United States dropped two atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945, causing Japan to surrender. Critics of the US decision to drop the bombs have argued that the US knew that Japan was about to surrender and that it was unnecessary to drop the bombs. They suggest that the US action was intended to stop the Soviet Union from making military and political gains in Asia and elsewhere and to show Moscow that the United States was supreme. US supporters have argued that the dropping of the atomic bombs was necessary to end the war quickly and to stop further loss of American and Allied lives. Whatever the motives, the consequence of the end of the Second World War was the rise of two new powers on the global stage. With the defeat of Germany and Japan, the devastation of Europe and in many other parts of the world, the United States and the Soviet Union became the greatest powers in the world with the ability to influence events anywhere on earth.
Q. When did the First World War start?
The demolition of Berlin Wall leading to the unification of Germany took place in
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
The Western alliance was formalized into an organization, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), which came into existence in April 1949. It was an association of twelve states which declared that armed attack on any one of them in Europe or North America would be regarded as an attack on all of them. Each of these states would be obliged to help the other. The eastern alliance, known as the Warsaw Pact, was led by the Soviet Union. It was created in 1955 and its principal function was to counter NATO’s forces in Europe. International alliances during the Cold War era were determined by the requirements of the superpowers and the calculations of the smaller states. As noted above, Europe became the main arena of conflict between the superpowers. In some cases, the superpowers used their military power to bring countries into their respective alliances. Soviet intervention in east Europe provides an example. The Soviet Union used its influence in eastern Europe, backed by the very large presence of its armies in the countries of the region, to ensure that the eastern half of Europe remained within its sphere of influence. In East and Southeast Asia and in West Asia (Middle East), the United States built an alliance system called — the Southeast Asian Treaty Organization (SEATO) and the Central Treaty Organization 1 (CENTO). The Soviet Union and communist China responded by having close relations with regional countries such as North Vietnam, North Korea and Iraq.
Q. What was the primary aim of Warsaw Pact?
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. In 1948, Burma was admitted to the United Nations and immediately supported the USA in the Cold War.
2. In 1948, Burma joined the United Nations, but refused to denounce China as the aggressor in the Korean War.
The Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union is the classic case of a _______________.
|
34 videos|246 docs|52 tests
|




















