Olympiad Test: Nutrition in Animals - Class 6 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Advance Learner Course: Science Class 6 - Olympiad Test: Nutrition in Animals
The semi-solid mass which is produced after thoroughly mix up of food and gastric juice is called
Which of the following component of food do not provide energy to body building?
The type of digestion which takes place within the cell is termed as
In amoeba, digestion of food takes place inside
Which one is the largest gland in the human body?
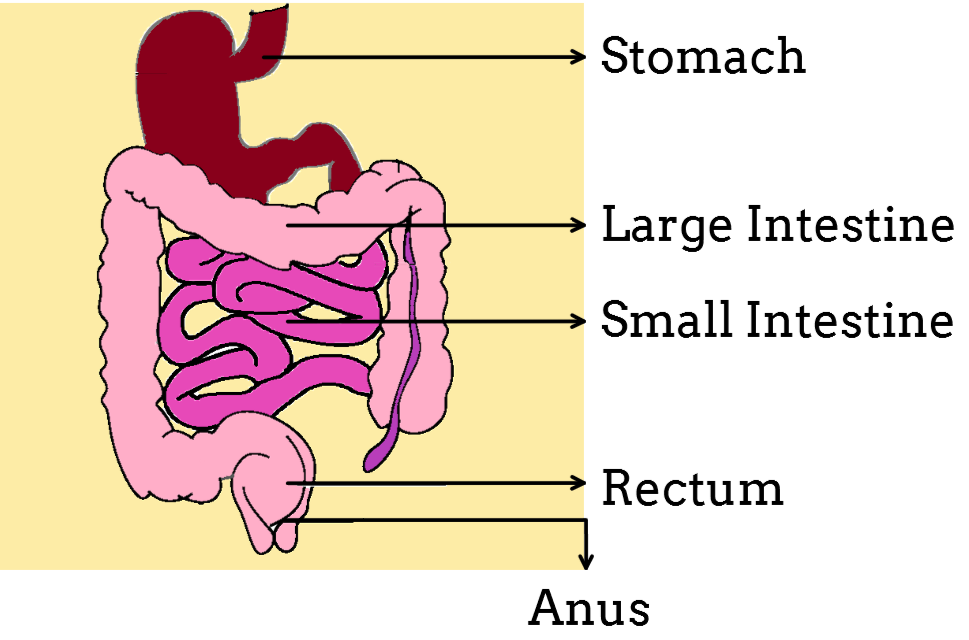
The inner walls of the small intestine have millions of small finger like projections called
The sharp teeth used for tearing food is called
Biological catalyst that breakdown the food into simpler form is called
Small intestine contain small finger-like projections to absorb digested food is called
Absorption of water in alimentary canal takes place in
Grass is rich in ________ a special kind of carbohydrate which can only be digested by ruminants.
|
26 videos|32 docs|9 tests
|