Test: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - 2 - Class 10 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Science Class 10 - Test: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - 2
The area around a magnet, in which its influence (force of attraction or repulsion) can be felt, is called its
Which device produces the electric current?
A constant current I flows through a horizontal metal wire in the plane of the paper from east to west as shown in the figure. The direction of magnetic field will be from north to south at a point :



What is that instrument which can detect the presence of electric current in a circuit?
The direction of magnetic field developed around a current-carrying conductor can be easily found by the use of
Who has stated the Right hand Thumb Rule?
The strength of the magnetic field around a current-carrying straight conductor
What should be the core of an electromagnet?
The strength of a magnetic field inside a long current-carrying straight solenoid coil is
The most important safety method used for protecting home appliances from short circuiting or overloading is
The strength of magnetic field along the axis of a solenoid coil :
The strength of magnetic field inside a long current carrying straight solenoid is
A current-carrying conductor is placed perpendicular to the direction of a uniform magnetic field. The direction of force acting on the conductor due to magnetic field is given by
Commercial electric motors do not use
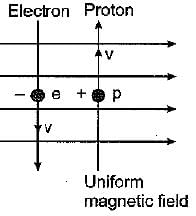
A uniform magnetic field exists in the plane of paper Electron Proton pointing from left to right as shown in the figure. In the field an electron and a proton move as shown. The electron and proton experience
For a current in a long straight solenoid N-pole and S-poIe are created at the two ends. Among the following statements, the incorrect statement is
Choose the wrong statement out of the following :
If the circuit is closed and magnetic field lines are drawn over the horizontal plane ABCD, the lines are
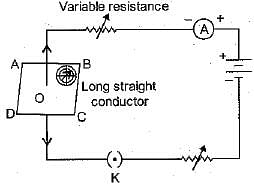
A boy was making a model of an electric bell. He connected the coil in the circuit and switched it on. However, the magnetism produced in the coil was not strong enough. He made some changes in the coil and the circuit was now working. What changes did the boy make in the coil?
|
83 videos|437 docs|74 tests
|


















