Test: Ray Optics & Optical Instruments - 3 - JEE MCQ
26 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Ray Optics & Optical Instruments - 3
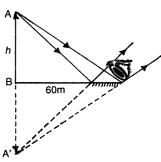
When a plane mirror AB is placed horizontally on level ground at a distance of 60 metres from the foot of a tower, the top of the tower and its image in the mirror subtends, an angle of 90° at B. The height of the tower is:

A unnumbered wall clock shows time 04 : 25 : 37, where 1st term represents hours, 2nd represents minutes & the last term represents seconds, What time will its image in a plane mirror show.
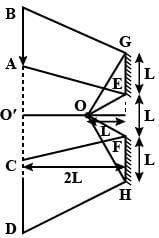
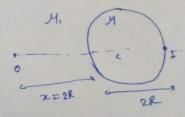
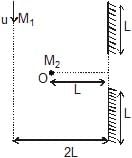
Two plane mirrors of length L are separated by distance L and a man M2 is standing at distance L from the connecting line of mirrors as shown in figure. A man M1 is walking in a straight line at distance 2L parallel to mirrors at speed u, then man M2 at O will be able to see image of M1 for total time :
A person is standing in a room of width 200 cm. A plane mirror of vertical length 10 cm is fixed on a wall in front of the person. The person looks into the mirror from distance 50 cm. How much width (height) of the wall behind him will he be able to see : (assume that he uses the full mirror)
Variation of focal length to form a sharp image on retina is called
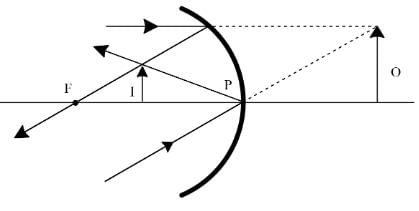
Which of the following cannot form real image of a real object ?
The radius of curvature of the left & right surface of the concave lens are 10 cm & 15 cm respectively. The radius of curvature of the mirror is 15 cm.
If a symmetrical biconcave thin lens is cut into two identical halves. They are placed in different ways as shown :
A convex lens forms an image of an object on screen. The height of the image is 9 cm. The lens is now displaced until an image is again obtained on the screen. The height of this image is 4 cm. The distance between the object and the screen is 90 cm.
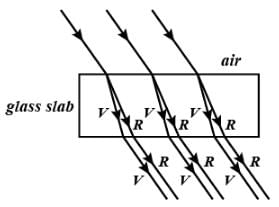
A narrow beam of white light goes through a slab having parallel faces
By properly combining two prisms made of different materials, it is possible to
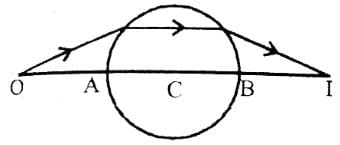
A transparent sphere of radius R and refractive index m. An object O is placed at a distance x from the pole of the first surface so that a real image is formed at the pole of the exactly opposite surface.
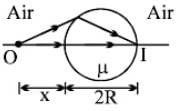
If x = 2R, then the value of m is
A transparent sphere of radius R and refractive index m. An object O is placed at a distance x from the pole of the first surface so that a real image is formed at the pole of the exactly opposite surface.
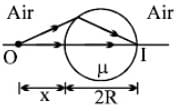
If x = ∞, then the value of m is
A transparent sphere of radius R and refractive index m. An object O is placed at a distance x from the pole of the first surface so that a real image is formed at the pole of the exactly opposite surface.
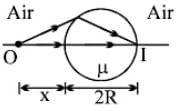
If an object is placed at a distance R from the pole of first surface, then the real image is formed at a distance R from the pole of the second surface. The refractive index m of the sphere is given by
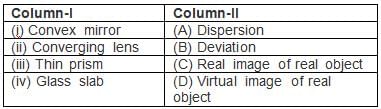
Column -II shows the optical phenomenon that can be associated with optical components given in column-I. Note that column-I may have more than one matching options in column-II.
Statement-I : If a source of light is placed in front of rough wall its image is not seen.
Statement-II : The wall does not reflect light.
Statement-I : As the distance x of a parallel ray from axis increases, focal length decreases
Statement-II : As x increases, the distance from pole to the point of intersection of reflected ray with principal axis decreases
Statement-I : When an object dipped in a liquid is viewed normally, the distance between the image and the object is indepedent of the height of the liquid above the object.
Statement-II : The normal shift is independent of the location of the slab between the object and the observer.
Statement-I : When two plane mirrors are kept perpendicular to each other as shown ( O si the point object), 3 image will be formed.
Statement-II : In case of multiple reflection, image of one surface can act as an object for the next surface.
Statement-I : A piece of paper placed at the position of a real image of a virtual object of intense light will burn after sufficient time.
Statement-II : A virtual object is that point where the incident rays appear to converge and a real image is that point at which reflected/ refracted rays actually converge.
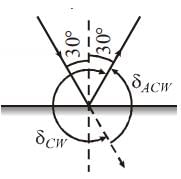
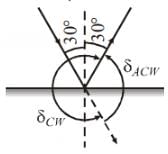
Find the angle of deviation (clockwise) suffered by a ray incident on a plane mirror, at an angle of incidence 30°.
Find the angle of deviation (anticlockwise) suffered by a ray incident on a plane mirror, at an angle of incidence 30°.
Figure shows a plane mirror onto which a light ray is incident. If the incident light ray is turned by 10° and the mirror by 20°, as shown, find the angle turned by the reflected ray.
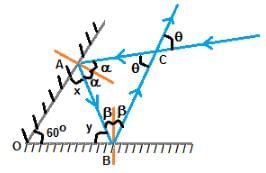
A light ray is incident on a plane mirror, which after getting reflected strikes another plane mirror, as shown in figure. The angle between the two mirrors is 60°. Find the angle 'q' shown in figure.
Find focal length of mirror that forms an image 6.2 cm behind mirror of an object placed at 26 cm in front of mirror?
There are two plane mirror inclined at 40°, as shown. A ray of light is incident on mirror M1. What should be the value of angle of incidence 'i' so that the light ray retraces its path after striking the mirror M2.