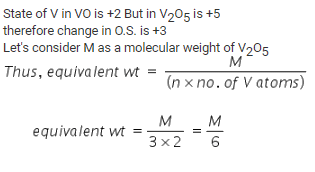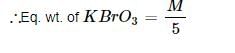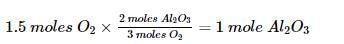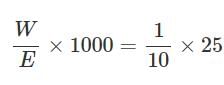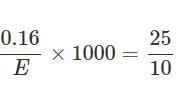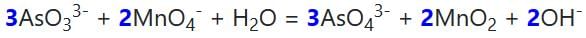Test: Mole Concept, Volumetric & Redox - 1 - Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Mole Concept, Volumetric & Redox - 1
4.4g of CO2 and 2.24 litre of H2 at STP (273.15 K and 1 atm pressure) are mixed in a container. The total of molecules present in the container will be
4I– + Hg2+ → HgI42– ; 1 mole of each Hg2+ and I– will form:
How many grams of I2 are present in a solution which requires 40 ml of 0.11N Na2S2O3 to react with it via the reaction:
S2O32– + I2 → S4O62– + 2I–?
S2O32– + I2 → S4O62– + 2I–?
Two elements A (atomic mass = 75) and B (atomic mass = 16) combine to yield a compound. The % by weight of A in the compound was found to be 75.08. The formula of compound is:
What weight of HNO3 is needed to convert 5g of Iodine into Iodic acid according to the reaction:
I2 + HNO3→ HIO3 + NO2 +H2O
In the reaction, VO + Fe2O3 → FeO + V2O5, the equilvalent weight of V2O5 is equal to its
When BrO3– ion reacts with Br– ion in acid solution Br2 is liberated. The eq. weight of KBrO3 in this reaction is:
10e + 2Br5+ → Br02
The hydrated salt, Na2SO4.nH2O, undergoes 55.9 % loss in weight on heating and become anhydrous. The value of n will be:
When a metal is burnt, its weight is increased by 24%. The eq. weight of the metal will be:
One mole of potassium chlorate is thermally decomposed and excess of aluminum is burnt in the gaseous product .How many moles of aluminum oxide are formed?
How much Cl2 at STP is liberated when one mole of KMnO4 reacts with HCl ?
Minimum quantity of H2S needed to precipitate 63.5g of Cu2+ is nearly:
2g of CaCO3 was treated with 0.1M HCl (500 ml). The volume of CO2 evolved at STP after heating the solution is:
10g of limestone on heating produces 4.2g of CaO. the percentage purity of CaCO3 in limestone is:
‘x’ g of KClO3 on decomposition gives ‘y’ ml of O2 at STP. The % purity of KClO3 would be
33.6g of an impure sample of sodium bicarbonate when heated strongly gave 4.4g of CO2. The % purity of NaHCO3 would be:
0.16g of dibasic acid required 25ml of N/10 NaOH for complete neutralization. Molecular wt. of acid is:
The molar coefficients of AsO33– and MnO4- in the reaction are:
AsO33– + MnO4Θ → AsO43– + MnO2
Which of the following is a disproportionation reaction?
Hydrogen and oxygen combine to form H2O2 and H2O containing 5.93% and 11.2 % hydrogen respectively. The data illustrates:


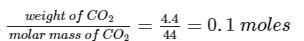
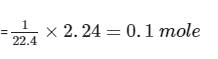
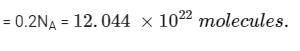

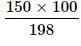 = 75.08g of A
= 75.08g of A