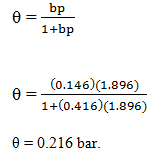Test: Adsorption - 1 - Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Adsorption - 1
For adsorption of gas on solid surface, the plots of log x/m vs. log P is linear with a slope equal to:
According to Langmuir adsorption isotherm the amount of gas adsorbed at very high pressure:
Adsorption of a gas on solid metal surface is spontaneous and exothermic, then:
Surface area available for adsorption per g of catalyst is called:
Plots of log vs. log C showing a straight line parallel to X-axis reveals that:
The Langmuir adsorption isotherm is deduced using the assumption:
Adsorption of methane follows the Langmuir adsorption isotherm at 90K. If p = 1.896cm3g-1bar-1 and b = 0.146bar-1. Calculate the value of θ.
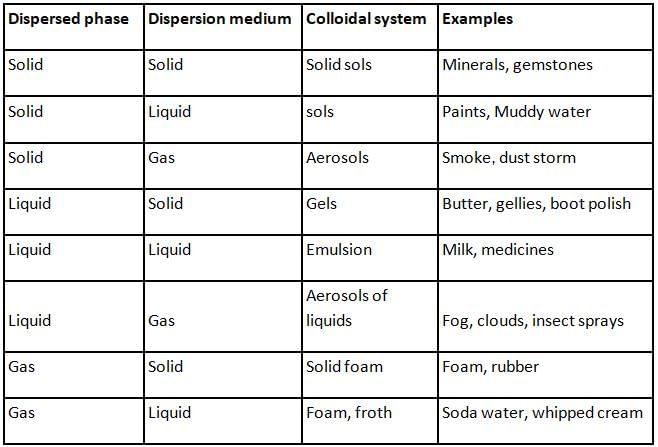
The continuous zig-zag movement of colloidal particles in a dispersion medium is called
Which of the following isotherm is applicable to physical adsorption?
Which of the following is not characteristic of chemisorption?