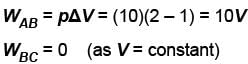First Law Of Thermodynamics MCQ Level - 2 (Part - 2) - Physics MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Topic wise Tests for IIT JAM Physics - First Law Of Thermodynamics MCQ Level - 2 (Part - 2)
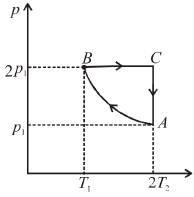
Two moles of an ideal monoatomic gas is taken through a cycle ABCA as shown in the p-T diagram. During the process AB, Pressure and temperature of the gas vary such that pT = constant. If T1 = 300K then the work done on the gas in the process AB is
Select one:

Select one:
One mole of a perfect gas is compressed adiabatically. The initial pressure and volume of the gas are 105N/m and 6L respectively. The final volume of the gas is 2L, molar specific heat of the gas at constant volume is 3R/2. The total work done is
Select one:
Select one:
Two identical containers A and B with frictionless pistons contains the same ideal gas at the same temperature and the same volume V. The mass of the gas in A is mA and that in B is mB . The gas in each cylinder is now allowed to expand isothermally to the final volume 2V. The changes in the pressure in A and B are found to be Δp and 1.5 Δp respectively. Then
Select one:
Select one:
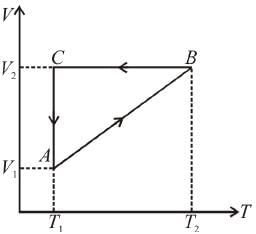
A cyclic process ABCA shown in the V-T diagram is performed with a constant mass of an ideal gas. Show the same process on a P-V diagram
Select one:
An ideal gas having initial pressure P, volume V and temperature T is allowed to expand adiabatically until its volume becomes 5.66V and its temperature falls to T/2. How many degree of freedom do the gas molecules have?
An ideal gas has specific heat at constant pressure 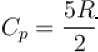 The gas is kept in a closed vessel of volume 0.00833m , at a temperature of 300K and a pressure of 1.6 × 106N/m2. An amount of 2.49 × 104J of heat energy is supplied to the gas.
The gas is kept in a closed vessel of volume 0.00833m , at a temperature of 300K and a pressure of 1.6 × 106N/m2. An amount of 2.49 × 104J of heat energy is supplied to the gas.
The final pressure and temperature of the gas are
Select one:
A monoatomic ideal gas, initially at temperature T1, is enclosed in a cylinder fitted with a frictionless piston. The gas is allowed to expand adiabatically to a temperature T2 by releasing the piston suddenly. If L1 and L2 are the lengths of the gas column before and after expansion respectively, then T1 /T2 is given by
Select one:
p-V plots for two gas during adiabatic process are shown in the figure. Plots 1 and 2 should correspond respectively to

Select one:
Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B is
Select one:
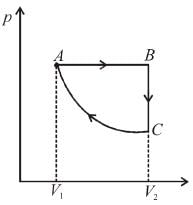
An ideal gas is taken through the cycle A → B → C → A a shown in the figure. If the net heat supplied to the gas in the cycle is 5J, the work done by the gas in the process C → A is
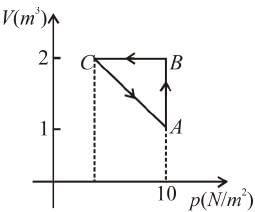


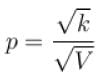
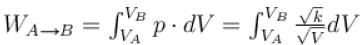
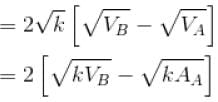
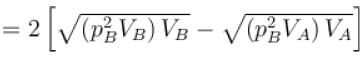
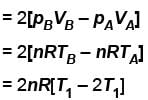
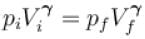
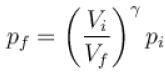
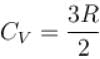
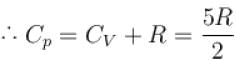
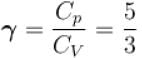
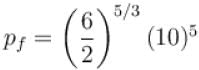
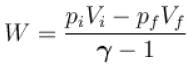
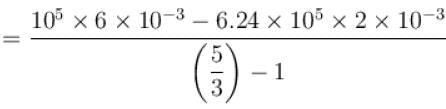

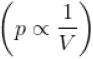 volume is increasing, therefore, pressure will decrease.
volume is increasing, therefore, pressure will decrease.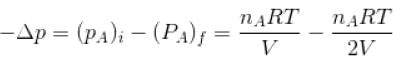
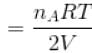 ...(i)
...(i)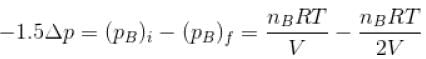
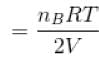 ...(ii)
...(ii)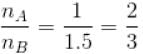
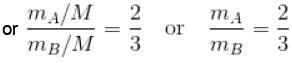
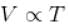
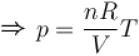 [V is constant]
[V is constant]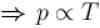
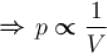

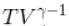 = constant
= constant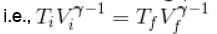
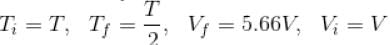
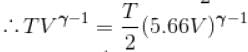
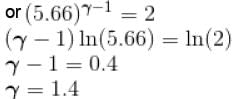
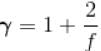
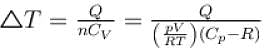
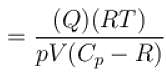
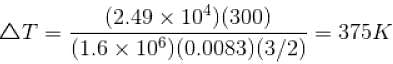
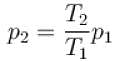
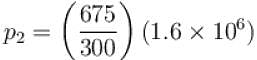
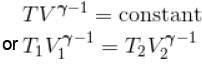

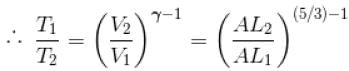 (A = Area of cross-section of piston)
(A = Area of cross-section of piston)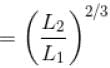
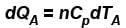 ...(i)
...(i)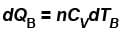 ...(ii)
...(ii)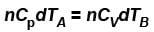
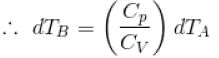
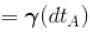 [
[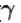 = 1.4 (diatomic)] (dTA = 30 K)
= 1.4 (diatomic)] (dTA = 30 K)