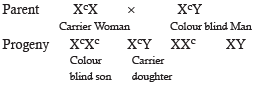31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Principles of Inheritance & Variation - 3 - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - 31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Principles of Inheritance & Variation - 3
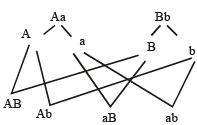
A human male produces sperms with the genotypes AB, Ab, aB, and ab pertaining to two diallelic characters in equal proportions. What is the corresponding genotype of this person?
[2007]
Inheritances of skin colour in humans is an example of
[2007]
The two polynucleotide chains in DNA are
[2007]
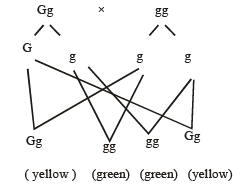
In pea plants, yellow seeds are dominant to green. If a heterozygous yellow seeded plant is crossed with a green seeded plant, what ratio of yellow and green seeded plants would you expect in F1 generation ?
[2007]
Two genes R and Y are located very close on the chromosomal linkage map of maize plant. When RRYY and rryy genotypes are hybridized, the F2 segregation will show
[2007]
A common test to find the genotype of a hybrid is by
[2007]
How many different kinds of gametes will be produced by a plant having the genotype AABbCC ?
[2006]
Phenotype of an organism is the result of
[2006]
Test cross involves
[2006]
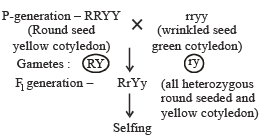
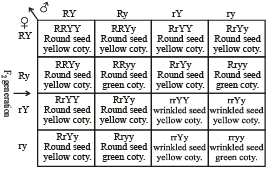
In Mendel’s experiment with garden pea, round seed shape (RR) was dominant over wrinkled seeds (rr), yellow cotyledon (YY) was dominant over green cotyledon (yy). What are the expected phenotypes in the F2 generation of the cross RRYY × rryy?
[2006]
Sickle cell anaemia has not been eliminated from the African population because
[2006]
Both sickle cell anemia and Huntington's chorea are
[2006]
Cri-du-chat syndrome in humans is caused by the
[2006]
Which one of the following is an example of polygenic inheritance ?
[2006]
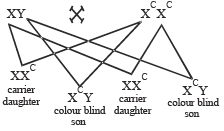
If a colour blind woman marries a normal visioned man, their sons will be
[2006]
Haemophilia is more commonly seen in human males than in human females because:
[2005]
A women with 47 chromosomes due to three copies of chromosome 21 is characterized by:
[2005]
Which of the following is not a hereditary disease?
[2005]
A woman with normal vision, but whose father was colour blind, marries a colour blind man. Suppose that the fourth child of this couple was a boy. This boy
[2005]
G-6-P dehydrogenase deficiency is associated with haemolysis of:
[2005]
The salivary gland chromosomes in the dipteran larvae, are useful in gene mapping because:
[2005]
At a particular locus, frequency of ‘A’ allele is 0.6 and that of ‘a’ is 0.4. What would be the frequency of heterozygotes in a random mating population at equilibrium?
[2005]
In order to find out the different types of gametes produced by a pea plant having the genotype AaBb, it should be crossed to a plant with the genotype:
[2005]
A self-fertilizing trihybrid plant forms
[2004]
After a mutation at a geneticlocus the character of an organism changes due to the change in
[2004]
|
9 docs|806 tests
|