Case Based Questions Test: Principles of Inheritance & Variation - 2 - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Case Based Questions Test: Principles of Inheritance & Variation - 2
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
Sickle cell anaemia is a genetic disorder where the body produces an abnormal haemoglobin called haemoglobins. Red blood cells are normally flexible and round, but when the haemoglobin is defective, blood cells take on a “sickle” or crescent shape. Sickle cell anaemia is caused by mutations in a gene called HBB.
It is an inherited blood disorder that occurs if both the maternal and paternal copies of the HBB gene are defective. In other words, if an individual receives just one copy of the defective HBB gene, either from mother or father, then the individual has no sickle cell anaemia but has what is called “sickle cell trait”. People with sickle cell trait usually do not have any symptoms or problems but they can pass the mutated gene onto their children. Three inheritance scenarios can lead to a child having sickle cell anaemia :
— Both parents have sickle cell trait
— One parent has sickle cell anaemia and the other has sickle cell trait
— Both parents have sickle cell anaemia
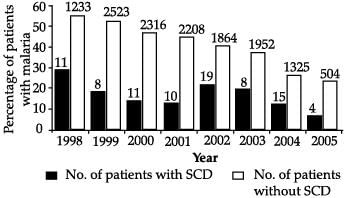
The following statements are drawn as conclusions from the above data (Kenya).
I. Patients with SCD (Sickle Cell Disease) are less likely to be infected with malaria.
II. Patients with SCD (Sickle Cell Disease) are more likely to be infected with malaria.
III. Over the years the percentage of people infected with malaria has been decreasing.
IV. Year 2000 saw the largest percentage difference between malaria patients with and without SCD.
Choose from below the correct alternative.

Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
Sickle cell anaemia is a genetic disorder where the body produces an abnormal haemoglobin called haemoglobins. Red blood cells are normally flexible and round, but when the haemoglobin is defective, blood cells take on a “sickle” or crescent shape. Sickle cell anaemia is caused by mutations in a gene called HBB.
It is an inherited blood disorder that occurs if both the maternal and paternal copies of the HBB gene are defective. In other words, if an individual receives just one copy of the defective HBB gene, either from mother or father, then the individual has no sickle cell anaemia but has what is called “sickle cell trait”. People with sickle cell trait usually do not have any symptoms or problems but they can pass the mutated gene onto their children. Three inheritance scenarios can lead to a child having sickle cell anaemia :
— Both parents have sickle cell trait
— One parent has sickle cell anaemia and the other has sickle cell trait
— Both parents have sickle cell anaemia
If both parents have sickle cell trait, then there is _______________of the child having sickle cell anaemia.
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
Sickle cell anaemia is a genetic disorder where the body produces an abnormal haemoglobin called haemoglobins. Red blood cells are normally flexible and round, but when the haemoglobin is defective, blood cells take on a “sickle” or crescent shape. Sickle cell anaemia is caused by mutations in a gene called HBB.
It is an inherited blood disorder that occurs if both the maternal and paternal copies of the HBB gene are defective. In other words, if an individual receives just one copy of the defective HBB gene, either from mother or father, then the individual has no sickle cell anaemia but has what is called “sickle cell trait”. People with sickle cell trait usually do not have any symptoms or problems but they can pass the mutated gene onto their children. Three inheritance scenarios can lead to a child having sickle cell anaemia :
— Both parents have sickle cell trait
— One parent has sickle cell anaemia and the other has sickle cell trait
— Both parents have sickle cell anaemia
If one parent has sickle cell anaemia and the other has sickle cell trait, there is __________that their children will have sickle cell anaemia and ___________will have sickle cell trait.
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
Sickle cell anaemia is a genetic disorder where the body produces an abnormal haemoglobin called haemoglobins. Red blood cells are normally flexible and round, but when the haemoglobin is defective, blood cells take on a “sickle” or crescent shape. Sickle cell anaemia is caused by mutations in a gene called HBB.
It is an inherited blood disorder that occurs if both the maternal and paternal copies of the HBB gene are defective. In other words, if an individual receives just one copy of the defective HBB gene, either from mother or father, then the individual has no sickle cell anaemia but has what is called “sickle cell trait”. People with sickle cell trait usually do not have any symptoms or problems but they can pass the mutated gene onto their children. Three inheritance scenarios can lead to a child having sickle cell anaemia :
— Both parents have sickle cell trait
— One parent has sickle cell anaemia and the other has sickle cell trait
— Both parents have sickle cell anaemia
Sickle cell anaemia is a/an ________________ disease.
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
Sickle cell anaemia is a genetic disorder where the body produces an abnormal haemoglobin called haemoglobins. Red blood cells are normally flexible and round, but when the haemoglobin is defective, blood cells take on a “sickle” or crescent shape. Sickle cell anaemia is caused by mutations in a gene called HBB.
It is an inherited blood disorder that occurs if both the maternal and paternal copies of the HBB gene are defective. In other words, if an individual receives just one copy of the defective HBB gene, either from mother or father, then the individual has no sickle cell anaemia but has what is called “sickle cell trait”. People with sickle cell trait usually do not have any symptoms or problems but they can pass the mutated gene onto their children. Three inheritance scenarios can lead to a child having sickle cell anaemia :
— Both parents have sickle cell trait
— One parent has sickle cell anaemia and the other has sickle cell trait
— Both parents have sickle cell anaemia
If both parents have sickle cell trait, then there is _______________of the child having sickle cell trait.
Read the following and answer the questions given below:
Turner’s syndrome is an example of monosomy. It is formed by the union of an allosome free egg and a normal ‘X’ containing sperm or a normal egg and an allosome free sperm. The individual has 2n = 45 chromosomes (44 + X0) instead of 46. Such individuals are sterile females who have rudimentary ovaries, under developed breasts, small uterus, short stature, webbed neck and abnormal intelligence. They may not menstruate or ovulate. This disorder can be treated by giving female sex hormone to the women from the age of puberty to make them develop breasts and have menstruation. This makes them feel more normal.
Assertion : Turners syndrome is caused due to absence of any one of the X and Y sex chromosome.
Reason : Individuals suffering from Turner 'syndrome show masculine as well as feminine development.
Read the following and answer the questions given below:
Turner’s syndrome is an example of monosomy. It is formed by the union of an allosome free egg and a normal ‘X’ containing sperm or a normal egg and an allosome free sperm. The individual has 2n = 45 chromosomes (44 + X0) instead of 46. Such individuals are sterile females who have rudimentary ovaries, under developed breasts, small uterus, short stature, webbed neck and abnormal intelligence. They may not menstruate or ovulate. This disorder can be treated by giving female sex hormone to the women from the age of puberty to make them develop breasts and have menstruation. This makes them feel more normal.
Turner’s syndrome is an example of
Read the following and answer the questions given below:
Turner’s syndrome is an example of monosomy. It is formed by the union of an allosome free egg and a normal ‘X’ containing sperm or a normal egg and an allosome free sperm. The individual has 2n = 45 chromosomes (44 + X0) instead of 46. Such individuals are sterile females who have rudimentary ovaries, under developed breasts, small uterus, short stature, webbed neck and abnormal intelligence. They may not menstruate or ovulate. This disorder can be treated by giving female sex hormone to the women from the age of puberty to make them develop breasts and have menstruation. This makes them feel more normal.
Which of the following statements regarding Turner’s syndrome is incorrect?
Read the following and answer the questions given below:
Turner’s syndrome is an example of monosomy. It is formed by the union of an allosome free egg and a normal ‘X’ containing sperm or a normal egg and an allosome free sperm. The individual has 2n = 45 chromosomes (44 + X0) instead of 46. Such individuals are sterile females who have rudimentary ovaries, under developed breasts, small uterus, short stature, webbed neck and abnormal intelligence. They may not menstruate or ovulate. This disorder can be treated by giving female sex hormone to the women from the age of puberty to make them develop breasts and have menstruation. This makes them feel more normal.
Number ot barr body present in a female with Turners syndrome is
Read the following and answer the questions given below:
Turner’s syndrome is an example of monosomy. It is formed by the union of an allosome free egg and a normal ‘X’ containing sperm or a normal egg and an allosome free sperm. The individual has 2n = 45 chromosomes (44 + X0) instead of 46. Such individuals are sterile females who have rudimentary ovaries, under developed breasts, small uterus, short stature, webbed neck and abnormal intelligence. They may not menstruate or ovulate. This disorder can be treated by giving female sex hormone to the women from the age of puberty to make them develop breasts and have menstruation. This makes them feel more normal.
Turner’s syndrome is a/an
Read the following and answer the questions given below:
Haemophilia is a sex linked disease which is also known as bleeder’s disease as the patient will continue to bleed even from a minor cut since he or she does not possess the natural phenomenon of blood clotting due to absence of anti-haemophilic globulin or factor VIII and plasma thromboplastin factor IX essential for it. As a result of continuous bleeding the patient may die of blood loss. Colour blindness is another type of sex linked trait in which the eye fails to distinguish red and green colours. Vision is however, not affected and the colour blind can, lead a normal life, reading, writing and driving (distinguishing traffic lights by their position).
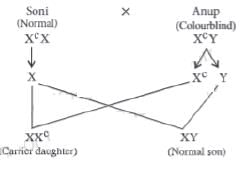
Anup is having colourblindness and is married to Soni who is normal. What is the chance that their son will have the disease?
Read the following and answer the questions given below:
Haemophilia is a sex linked disease which is also known as bleeder’s disease as the patient will continue to bleed even from a minor cut since he or she does not possess the natural phenomenon of blood clotting due to absence of anti-haemophilic globulin or factor VIII and plasma thromboplastin factor IX essential for it. As a result of continuous bleeding the patient may die of blood loss. Colour blindness is another type of sex linked trait in which the eye fails to distinguish red and green colours. Vision is however, not affected and the colour blind can, lead a normal life, reading, writing and driving (distinguishing traffic lights by their position).
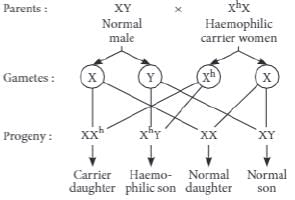
A man whose father was colourblind and mother was normal marries a woman whose father was haemophilic and mother was normal. Which of the following is true for their progenies? [Note: Percentage is from the total number of progenies.]
Read the following and answer the questions given below:
Haemophilia is a sex linked disease which is also known as bleeder’s disease as the patient will continue to bleed even from a minor cut since he or she does not possess the natural phenomenon of blood clotting due to absence of anti-haemophilic globulin or factor VIII and plasma thromboplastin factor IX essential for it. As a result of continuous bleeding the patient may die of blood loss. Colour blindness is another type of sex linked trait in which the eye fails to distinguish red and green colours. Vision is however, not affected and the colour blind can, lead a normal life, reading, writing and driving (distinguishing traffic lights by their position).
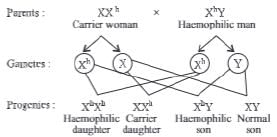
If a haemophilic man marries a woman whose father was haemophilic and mother was normal then which of the following holds true for their progenies?
Read the following and answer the questions given below:
Haemophilia is a sex linked disease which is also known as bleeder’s disease as the patient will continue to bleed even from a minor cut since he or she does not possess the natural phenomenon of blood clotting due to absence of anti-haemophilic globulin or factor VIII and plasma thromboplastin factor IX essential for it. As a result of continuous bleeding the patient may die of blood loss. Colour blindness is another type of sex linked trait in which the eye fails to distinguish red and green colours. Vision is however, not affected and the colour blind can, lead a normal life, reading, writing and driving (distinguishing traffic lights by their position).
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding haemophilia?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason.
Assertion: In F2 generation of plant Mirabilis jalapa, the pink coloured flowers appear.
Reason: This is observed due epistatic suppression of white colour alleles in one of parental flowers by red colour alleles.
|
78 videos|277 docs|174 tests
|