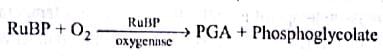Test: Biosynthetics Phase - ACT MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Biosynthetics Phase
Which of the following statement about dark reaction is correct?
Which of the following products of the light reaction are subsequently used during the biosynthetic phase of photosynthesis?
Refer to the given diagrammatic of an electron micrograph of a section of chloroplast.
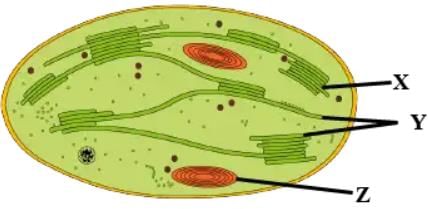
Select the option which correctly depicts the function of parts X, Y and Z.

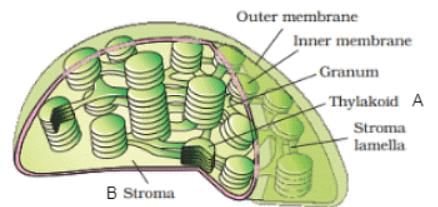
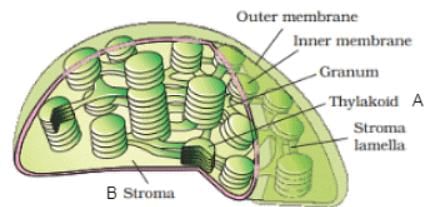
A sectional view of the chloroplast is given below. Choose the correct statement for A and B?
Read the given statement and select the correct option.
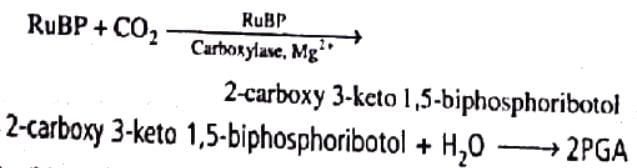
Statement 1: Carboxylation is the most crucial step of Calvin where CO2 is utilised for the carboxylation of RuBP.
Statement 2: This reaction is catalysed by the enzyme RuBisCO which results in the formation of two molcules of 3-PGA.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Crassulacean acid metabolism occurs in succulent plants which grow in xeric conditions.
Statement 2 : Stomata are generally sunken in succulent plants.
Kranz anatomy is not exhibited by which of the following plants?
Given figure represents C4 pathway. Select the suitable option for A, B and C.

During fixation of one molecule of CO2 by C3 plants, number of ATP and NADPH2 required are
Which of the following statement is incorrect regarding the Calvin cycle of C3 plants?
Select the incorrect statement as far as kranz anatomy is concerned.
Optimum temperature conditions for photosynthesis in C3 and C4 plants are respectively
In an experiment in which photosynthesis is performed during the day you provide a plant with radioactive carbon dioxide (14CO2) as a metabolic tracer. The 14C is incorporated first into oxaloacetic acid. The plant is best characterised as a
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Photorespiration interferes with the successful functioning of Calvin cycle.
Statement 2: Photorespiration oxidises ribulose-1,5 biphosphate which is an acceptor of CO2 in Calvin cycle.
How many ATP and NADPH2 are respectively produced in the process of photorespiration?
Which organelle out of these does not participate in photorespiration?
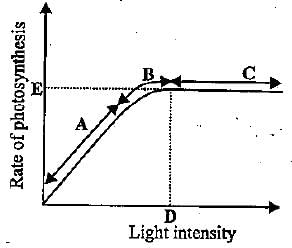
Study the given graph showing the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis. Which of the following statement regarding this is correct?
The law of limiting factors' was given by _______ in the year _______.
Given table shows the CO2 compensation point and optimum CO2 concentration for phtosynthesis for C3 and C4 plants.
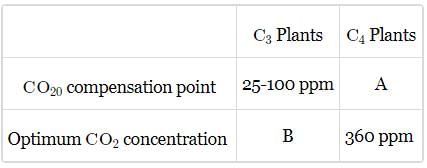
Select the correct values for A and B.
When the temperature is increased from minimum to optimum, rate of photosynthesis doubles for every _______ rise in temperature.
Tropical plants have a ______ temperature optimum than the plants adapted to temperate climates.
One scientist cultured Cladophora in a suspension of Azotobacter and illuminated the culture by splitting light through a prism. He observed that bacteria accumulated mainly in the region of: