Test: Common Diseases in Humans & Immunity - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Common Diseases in Humans & Immunity
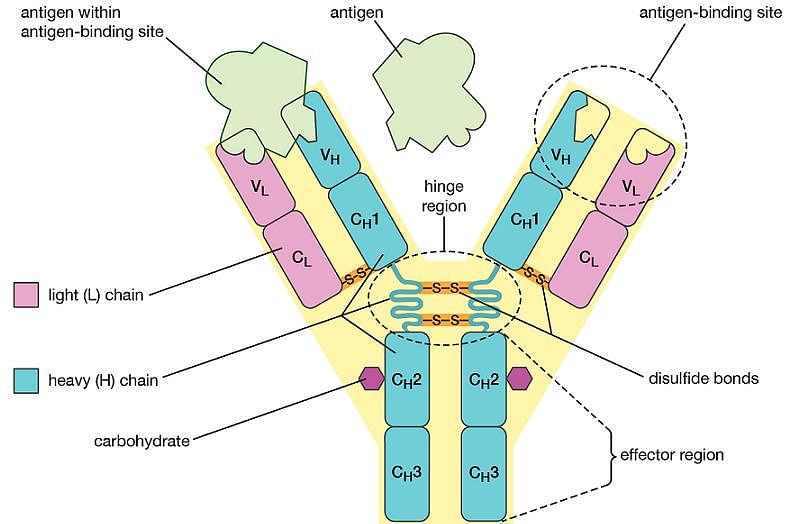
Antigenic determinant sites bind to which portion of an antibody molecule?
(1) Light chain
(2) Heavy chain
(3) Intermediate chains
(4) Plasma cells
(1) Light chain
(2) Heavy chain
(3) Intermediate chains
(4) Plasma cells
Formation of antibodies within our body is called:
Which lymphoid organ reduces in size as an individual ages and becomes quite small by the time of puberty?
The disease chikungunya is transmitted by:
Anti venom against snake poison contains:
The sporozoites that cause infection, when a female Anopheles mosquito bites a person, are stored in_________.
The organisms which cause diseases in plants and animals are called:
How are Infectious Diseases transmitted?
Assertion (A): Malaria is caused by a virus.
Reason (R): Malaria is transmitted to humans by the bite of infected Anopheles mosquitoes.
Which of the following is the unit of immune system?
Which of the following is a Congenital Disease?
Immuno-deficiency syndrome could develop due to:
The chemical test that is used for diagnosis of typhoid is:
|
78 videos|277 docs|174 tests
|